AI大模型学习
1、环境搭建
2、Embedding与向量数据库
3、RAG技术与应用
4、RAG高级技术与实践
5、LlamaIndex知识管理与信息检索
6、基于LlamaIndex开发的中医临床诊疗助手
7、LangChain多任务应用开发
8、Function Calling与Agent 智能体
9、Agent应用与图状态编排框架LangGraph
10、基于LangGraph实现智能分诊系统
11、MCP应用技术开发
12、AI 应用开发新范式 MCP 技术详解
13、基于LangGraph的多智能体交互系统
14、企业级智能分诊系统RAG项目
15、LangGraph与Agno-AGI深度对比分析
本文档使用 MrDoc 发布
-
+
首页
8、Function Calling与Agent 智能体
# Function Calling与Agent 智能体 ## 💡 学习目标 1. 理解Function Calling的概念 2. 理解Function Calling的工作原理 3. 实战使用OpenAI提供的Function Calling接口(基础请求及优化) 4. 探讨自定义Function的提供的可能性 5. 探讨Function Calling在大模型应用场景中带来的“质变” 6. 智能体/LLM应用的定义与作用 - 什么是智能体?智能体与大模型的关系是什么样的 - 智能体概念的演进过程,基本架构与功能 7. 智能体开发框架smolagents 8. Agentic RAG 实战 9. 智能体的应用场景 - 探讨智能体在行业场景中的落地情况 - 探讨智能体系统/LLM应用的常见分类 ## 1. Function Calling的概念 Function Calling(函数调用),顾名思义,为模型提供了一种调用函数的方法/能力。 - Function Calling成立的模型能力基础: - 问题理解和行动规划 - 结构化数据输出 - 上下文学习 In-Context Learning Function Calling让模型输出不再局限于自身推理输出,而是可以与外部系统交互,完成更复杂的任务 - 常见Function Calling应用场景包括: - 查询检索,补充额外信息(如RAG、搜索) - 理解用户输入,向外部系统写入信息(如表单填写) - 调用外部系统能力,完成实际行为动作(如下订单) ## 2. Function Calling的工作原理 ### 2.1 OpenAI官方定义 OpenAI官方说明文档:https://platform.openai.com/docs/guides/function-calling 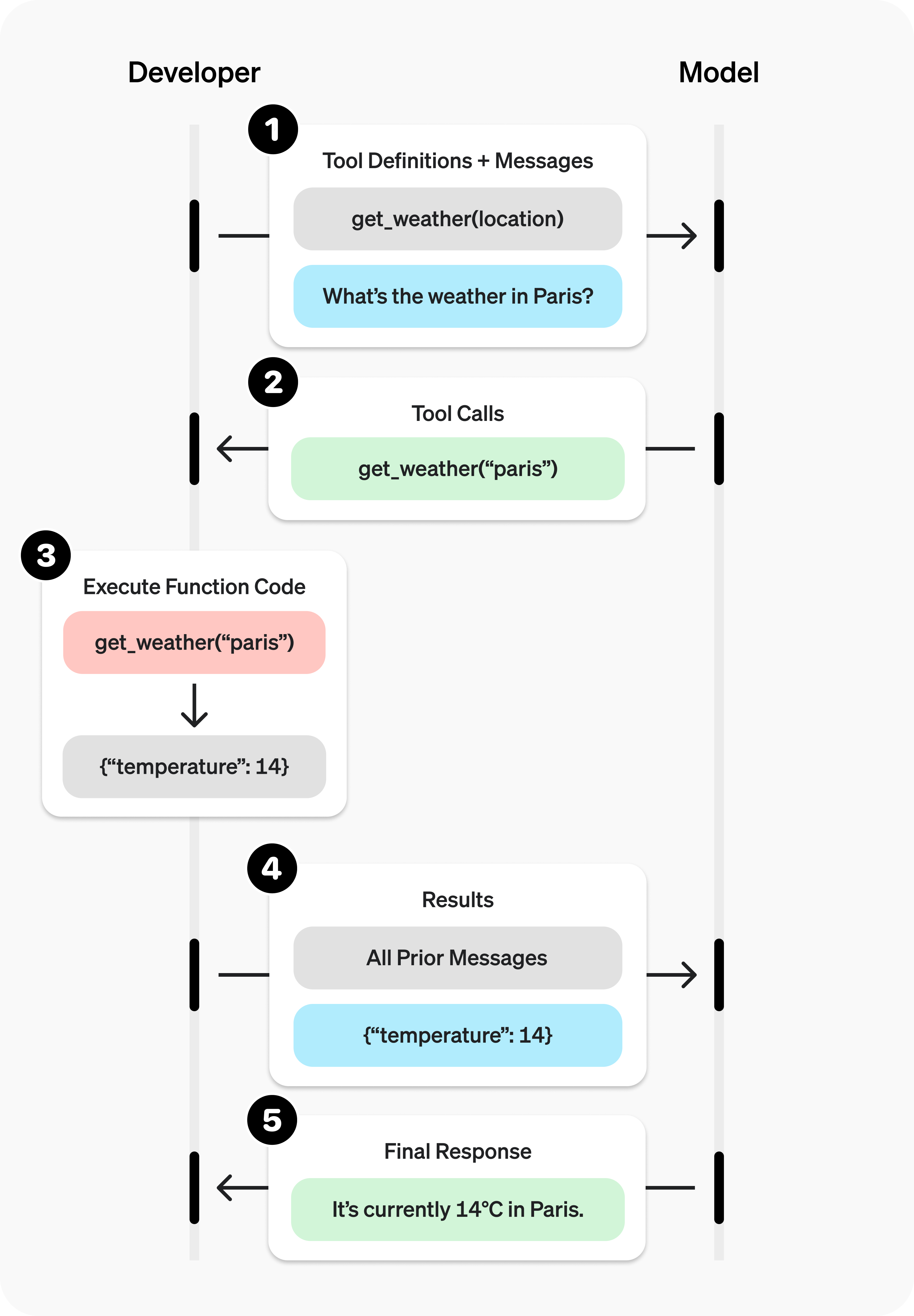 ### 2.2 描述Function Calling的另一个流程图 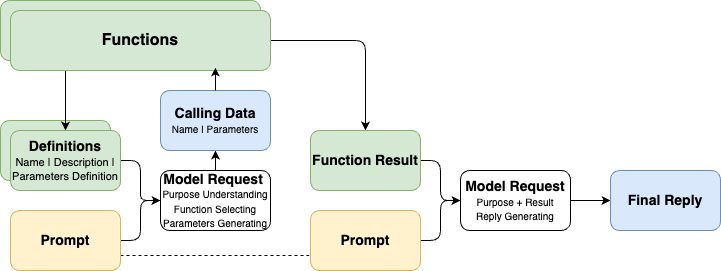 ### 2.3 Calling是结果,理解和选择才是第一步 - 除了代表用户诉求的Prompt之外,Function Calling还需要将可用的工具信息(Function Definitions)也提供给模型 - 在第一次请求时,模型的核心工作如下: 1. 理解Prompt所代表的“诉求”和Definitions所代表的“行动可能性” 2. “选择”完成“诉求”所需要进行的“行动”(从“行动可能性”中获得) 3. 根据所选择的“行动”,给出执行“行动”所需的“行动参数”(Parameters) - 那么想一想: 1. 什么影响“选择”的效果? 2. 什么影响“行动”的可执行性和效果? ### 2.4 作为可选项的结果回调和最终回复输出 - 在对话流中,将Function Calling的结果(Function Result)与初始的Prompt诉求再次组合,提供给模型以获得最终的回复输出,是常见的流程(RAG就是一个典型的例子) - 但如果我们将Function Calling用于非对话流场景,最终回复输出就不一定是必选项了,例如: 1. 【只需要完成Calling动作】我们只是希望通过Function Calling完成行动选择和发起,接下来就进入业务处理流程,例如:理解用户表达并代替用户下单 2. 【只需要完成行动参数Parameters生成】我们只是希望将Function Calling做好工具使用决策,并完成部分请求参数的生成,接下来需要走业务流程补全其他参数(比如鉴权信息),例如:敏感数据查询 在实际生产中,不给出最终回复输出,而只是使用Function Calling返回的调用方法数据,是很常见的用法。 ## 3. 实际调用Function Calling ### 从官方案例开始 #### 第一步:工具决策和调用信息生成 ```python import os from openai import OpenAI client = OpenAI( api_key=os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY"), base_url=os.getenv("OPENAI_BASE_URL"), ) # 给出工具定义 tools = [ # 每一个列表元素项,就是一个工具定义 { # 类型标注(固定格式) "type": "function", # 函数定义 "function": { # 函数名称(帮助我们去查找本地的函数在哪里,函数映射ID) "name": "get_weather", # 函数描述(帮助模型去理解函数的作用,适用场景,可以理解为Prompt的一部分) "description": "Get current temperature for provided coordinates in celsius.", # 函数依赖参数的定义(帮助模型去理解如果要做参数生成,应该怎么生成) "parameters": { # 参数形式 "type": "object", # 对应输出JSON String # 参数结构 "properties": { # 参数名,参数类型 "latitude": {"type": "number"}, # 参数名,参数类型 "longitude": {"type": "number"} }, # 必须保证生成的参数列表(每个元素对应上面properties的参数名) "required": ["latitude", "longitude"], "additionalProperties": False }, # 格式是否严格(默认为True) "strict": True } } ] # 给出诉求表达 messages = [{"role": "user", "content": "What's the weather like in Shanghai today?"}] #messages = [{"role": "user", "content": "How are you today?"}] #messages = [{"role": "user", "content": "请告诉我北京的经纬度"}] #messages = [{"role": "user", "content": "What's the weather like today?"}] # 发起请求 completion = client.chat.completions.create( model="gpt-4o", messages=messages, # 把工具定义提交给模型,就已经默认启用了Function Calling tools=tools, ) # print(completion.choices[0].message) # print(completion.choices[0].message.tool_calls[0].function) if completion.choices[0].message.tool_calls: print(completion.choices[0].message.tool_calls[0].function) else: print("No function is called.") # Function(arguments='{"latitude":31.2304,"longitude":121.4737}', name='get_weather') ``` ```python - 情况1:问与工具的无关的问题会发生什么? - `messages = [{"role": "user", "content": "How are you today?"}]` - 情况2:问无法获得确切行动参数的问题会发生什么? - `messages = [{"role": "user", "content": "What's the weather like today?"}]` - 如何容错: ```python if completion.choices[0].message.tool_calls: print(completion.choices[0].message.tool_calls[0].function) else: print("No function is called.") ``` ``` #### 第二步:实际调用工具 ```python function_calling_message = completion.choices[0].message function_calling = completion.choices[0].message.tool_calls[0] print("Call Function Name:", function_calling.function.name) print("Call Function Arguments:", function_calling.function.arguments) # Call Function Name: get_weather # Call Function Arguments: {"latitude":31.2304,"longitude":121.4737} ``` ```python import json def get_weather(*, latitude:float, longitude:float): return { "temperature": 23, "weather": "Sunny", "wind_direction": "South", "windy": 2, } functions = { "get_weather": get_weather } function_result = functions[function_calling.function.name](**json.loads(function_calling.function.arguments)) print(function_result) # {'temperature': 23, 'weather': 'Sunny', 'wind_direction': 'South', 'windy': 2} ``` #### 第三步:将结果返回给模型获取最终结果 ```python # 必须:让模型知道自己之前给了一个什么指令(包含tool_call_id) messages.append(function_calling_message) # 包含了tool_call_id的结果加入消息列 messages.append({ "role": "tool", "tool_call_id": function_calling.id, "content": str(function_result), }) print(messages) # [{'role': 'user', 'content': "What's the weather like in Shanghai today?"}, ChatCompletionMessage(content=None, refusal=None, role='assistant', annotations=[], audio=None, function_call=None, tool_calls=[ChatCompletionMessageToolCall(id='call_xSbiJ0Q4FnlANv8tMOsYRc1P', function=Function(arguments='{"latitude":31.2304,"longitude":121.4737}', name='get_weather'), type='function')]), {'role': 'tool', 'tool_call_id': 'call_xSbiJ0Q4FnlANv8tMOsYRc1P', 'content': "{'temperature': 23, 'weather': 'Sunny', 'wind_direction': 'South', 'windy': 2}"}] ``` ```python final_result = client.chat.completions.create( model="gpt-4o", messages=messages, tools=tools, ) print(final_result.choices[0].message.content) # The weather in Shanghai today is sunny with a temperature of 23°C. The wind is coming from the south at a speed of 2 km/h. ``` - 如果获得错误信息会怎么样? ```python error_messages = messages[:1] error_messages.append(function_calling_message) error_messages.append({ "role": "tool", "tool_call_id": function_calling.id, "content": str(TypeError("Key 'latitude' can not be supported any more, please use 'lat' instead.")), }) print(error_messages) final_result = client.chat.completions.create( model="gpt-4o", messages=error_messages, tools=tools, ) print(final_result.choices[0]) ``` - 答:会重试,但不多... ## 4. 在实际应用场景中的一些案例 ### 4.1 封装基本方法 ```python import os import json from typing import TypedDict from openai import OpenAI class FunctionCallingResult(TypedDict): name: str arguments: str class ModelRequestWithFunctionCalling: def __init__(self): self._client = OpenAI( api_key=os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY"), base_url=os.getenv("OPENAI_BASE_URL"), ) self._function_infos = {} self._function_mappings = {} self._messages = [] def register_function(self, *, name, description, parameters, function, **kwargs): self._function_infos.update({ name: { "type": "function", "function": { "name": name, "description": description, "parameters": parameters, **kwargs } } }) self._function_mappings.update({ name: function }) return self def reset_messages(self): self._messages = [] return self def append_message(self, role, content, **kwargs): self._messages.append({ "role": role, "content": content, **kwargs }) print("[Processing Messages]:", self._messages[-1]) return self def _call(self, function_calling_result:FunctionCallingResult): function = self._function_mappings[function_calling_result.name] arguments = json.loads(function_calling_result.arguments) return function(**arguments) def request(self, *, role="user", content=None): if role and content: self._messages.append({ "role": role, "content": content }) result = self._client.chat.completions.create( model="gpt-4o", messages=self._messages, tools=self._function_infos.values(), ) self.append_message(**dict(result.choices[0].message)) if result.choices[0].message.tool_calls: for tool_call in result.choices[0].message.tool_calls: call_result = self._call(tool_call.function) self.append_message("tool", str(call_result), tool_call_id=tool_call.id) return self.request() else: self.append_message("assistant", result.choices[0].message.content) return result.choices[0].message.content ``` ### 4.2 联网检索现实场景 ```python import requests import os import json amap_key = os.getenv("AMAP_MAPS_API_KEY") amap_base_url = "https://restapi.amap.com/v5" # 默认是 https://restapi.amap.com/v5 def get_location_coordinate(location, city): url = f"{amap_base_url}/place/text?key={amap_key}&keywords={location}®ion={city}" r = requests.get(url) result = r.json() if "pois" in result and result["pois"]: return result["pois"][0] return None def search_nearby_pois(longitude, latitude, keyword): url = f"{amap_base_url}/place/around?key={amap_key}&keywords={keyword}&location={longitude},{latitude}" r = requests.get(url) result = r.json() ans = "" if "pois" in result and result["pois"]: for i in range(min(3, len(result["pois"]))): name = result["pois"][i]["name"] address = result["pois"][i]["address"] distance = result["pois"][i]["distance"] ans += f"{name}\n{address}\n距离:{distance}米\n\n" return ans function_calling_request = ModelRequestWithFunctionCalling() ( function_calling_request .register_function( name="get_location_coordinate", description="根据POI名称,获得POI的经纬度坐标", parameters={ "type": "object", "properties": { "location": { "type": "string", "description": "POI名称,必须是中文", }, "city": { "type": "string", "description": "POI所在的城市名,必须是中文", } }, "required": ["location", "city"], }, function=get_location_coordinate, ) .register_function( name="search_nearby_pois", description="搜索给定坐标附近的poi", parameters={ "type": "object", "properties": { "longitude": { "type": "string", "description": "中心点的经度", }, "latitude": { "type": "string", "description": "中心点的纬度", }, "keyword": { "type": "string", "description": "目标poi的关键字", } }, "required": ["longitude", "latitude", "keyword"], }, function=search_nearby_pois, ) ) result = function_calling_request.request(content="五道口附近的咖啡馆") print("----------------------\n\n", result) ``` ```python [Processing Messages]: {'role': 'assistant', 'content': None, 'refusal': None, 'annotations': [], 'audio': None, 'function_call': None, 'tool_calls': [ChatCompletionMessageToolCall(id='call_CgPWqMF0iTsB3y7UDchAPE3e', function=Function(arguments='{"city":"北京","location":"五道口"}', name='get_location_coordinate'), type='function')]} [Processing Messages]: {'role': 'tool', 'content': "{'parent': '', 'address': '海淀区', 'distance': '', 'pcode': '110000', 'adcode': '110108', 'pname': '北京市', 'cityname': '北京市', 'type': '地名地址信息;热点地名;热点地名', 'typecode': '190700', 'adname': '海淀区', 'citycode': '010', 'name': '五道口', 'location': '116.338611,39.992552', 'id': 'B000A8WSBH'}", 'tool_call_id': 'call_CgPWqMF0iTsB3y7UDchAPE3e'} [Processing Messages]: {'role': 'assistant', 'content': None, 'refusal': None, 'annotations': [], 'audio': None, 'function_call': None, 'tool_calls': [ChatCompletionMessageToolCall(id='call_80oV9YDrCDQU4axygLZazpAE', function=Function(arguments='{"keyword":"咖啡馆","latitude":39.992552,"longitude":116.338611}', name='search_nearby_pois'), type='function')]} [Processing Messages]: {'role': 'tool', 'content': '星巴克(北京五道口购物中心店)\n海淀街道府路28号五道口商城1层\n距离:44米\n\n瑞幸咖啡(五道口购物中心店)\n成府路28号五道口购物中心负一层101号\n距离:67米\n\nManner Coffee(五道口购物中心店)\n成府路28号五道口购物中心1F层L1-04\n距离:88米\n\n', 'tool_call_id': 'call_80oV9YDrCDQU4axygLZazpAE'} [Processing Messages]: {'role': 'assistant', 'content': '在五道口附近,你可以找到以下咖啡馆:\n\n1. **星巴克(北京五道口购物中心店)** \n 地址:海淀街道府路28号五道口商城1层 \n 距离五道口约44米。\n\n2. **瑞幸咖啡(五道口购物中心店)** \n 地址:成府路28号五道口购物中心负一层101号 \n 距离五道口约67米。\n\n3. **Manner Coffee(五道口购物中心店)** \n 地址:成府路28号五道口购物中心1F层L1-04 \n 距离五道口约88米。\n\n这些咖啡馆都位于五道口购物中心内,非常方便。希望你能找到合适的休闲或工作的地方!', 'refusal': None, 'annotations': [], 'audio': None, 'function_call': None, 'tool_calls': None} [Processing Messages]: {'role': 'assistant', 'content': '在五道口附近,你可以找到以下咖啡馆:\n\n1. **星巴克(北京五道口购物中心店)** \n 地址:海淀街道府路28号五道口商城1层 \n 距离五道口约44米。\n\n2. **瑞幸咖啡(五道口购物中心店)** \n 地址:成府路28号五道口购物中心负一层101号 \n 距离五道口约67米。\n\n3. **Manner Coffee(五道口购物中心店)** \n 地址:成府路28号五道口购物中心1F层L1-04 \n 距离五道口约88米。\n\n这些咖啡馆都位于五道口购物中心内,非常方便。希望你能找到合适的休闲或工作的地方!'} ---------------------- 在五道口附近,你可以找到以下咖啡馆: 1. **星巴克(北京五道口购物中心店)** 地址:海淀街道府路28号五道口商城1层 距离五道口约44米。 2. **瑞幸咖啡(五道口购物中心店)** 地址:成府路28号五道口购物中心负一层101号 距离五道口约67米。 3. **Manner Coffee(五道口购物中心店)** 地址:成府路28号五道口购物中心1F层L1-04 距离五道口约88米。 这些咖啡馆都位于五道口购物中心内,非常方便。希望你能找到合适的休闲或工作的地方! ``` ### 4.3 本地数据库查询 #### 4.3.1 数据准备 ```python import sqlite3 database_schema_string = """ CREATE TABLE orders ( id INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL, -- 主键,不允许为空 customer_id INT NOT NULL, -- 客户ID,不允许为空 product_id STR NOT NULL, -- 产品ID,不允许为空 price DECIMAL(10,2) NOT NULL, -- 价格,不允许为空 status INT NOT NULL, -- 订单状态,整数类型,不允许为空。0代表待支付,1代表已支付,2代表已退款 create_time TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, -- 创建时间,默认为当前时间 pay_time TIMESTAMP -- 支付时间,可以为空 ); """ conn = sqlite3.connect(':memory:') cursor = conn.cursor() cursor.execute(database_schema_string) mock_data = [ (1, 1001, 'TSHIRT_1', 50.00, 0, '2023-09-12 10:00:00', None), (2, 1001, 'TSHIRT_2', 75.50, 1, '2023-09-16 11:00:00', '2023-08-16 12:00:00'), (3, 1002, 'SHOES_X2', 25.25, 2, '2023-10-17 12:30:00', '2023-08-17 13:00:00'), (4, 1003, 'SHOES_X2', 25.25, 1, '2023-10-17 12:30:00', '2023-08-17 13:00:00'), (5, 1003, 'HAT_Z112', 60.75, 1, '2023-10-20 14:00:00', '2023-08-20 15:00:00'), (6, 1002, 'WATCH_X001', 90.00, 0, '2023-10-28 16:00:00', None) ] for record in mock_data: cursor.execute(''' INSERT INTO orders (id, customer_id, product_id, price, status, create_time, pay_time) VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?) ''', record) conn.commit() def query_db(query): cursor.execute(query) return cursor.fetchall() ``` #### 4.3.2 调用执行 ```python function_calling_request = ModelRequestWithFunctionCalling() ( function_calling_request .register_function( name="query_db", description="使用此函数查询业务数据库获取结果,输出的SQL需要能够在Python的sqlite3中执行", parameters={ "type": "object", "properties": { "query": { "type": "string", "description": f""" SQL query extracting info to answer the user's question. The query should be returned in plain text, not in JSON. The query should only contain grammars supported by SQLite. """, } }, "required": ["query"], }, function=query_db, ) ) question = "2023年10月总共成交了几笔订单?" result = function_calling_request.request( content=f""" 问题:{ question }, 数据库元数据信息:{ database_schema_string }, """ ) ``` ```python [Processing Messages]: {'role': 'assistant', 'content': None, 'refusal': None, 'annotations': [], 'audio': None, 'function_call': None, 'tool_calls': [ChatCompletionMessageToolCall(id='call_OhYQtVIl3QPzJrIKdjCOKwts', function=Function(arguments='{"query":"SELECT COUNT(*) FROM orders WHERE strftime(\'%Y-%m\', create_time) = \'2023-10\';"}', name='query_db'), type='function')]} [Processing Messages]: {'role': 'tool', 'content': '[(4,)]', 'tool_call_id': 'call_OhYQtVIl3QPzJrIKdjCOKwts'} [Processing Messages]: {'role': 'assistant', 'content': '2023年10月总共成交了4笔订单。', 'refusal': None, 'annotations': [], 'audio': None, 'function_call': None, 'tool_calls': None} [Processing Messages]: {'role': 'assistant', 'content': '2023年10月总共成交了4笔订单。'} ``` ### 4.4 跨模型协作 #### 利用文心4.0以上模型作为搜索工具 ```python ##### 安装文心调用SDK # !pip install erniebot ``` 测试 ```python import os import erniebot erniebot.api_type = "aistudio" erniebot.access_token = os.getenv("AISTUDIO_ACCESS_TOKEN") # 访问aistudio.baidu.com注册账号,可获得自己的access_token response = erniebot.ChatCompletion.create( model="ernie-4.5-turbo-32k", messages=[{ "role": "user", "content": "GPT-5发布会有哪些亮点?" }]) print(response.get_result()) ``` ```python import os from openai import OpenAI client = OpenAI( api_key=os.getenv("AISTUDIO_ACCESS_TOKEN"), # Access Token属于个人账户的重要隐私信息,请谨慎管理,切忌随意对外公开, base_url="https://aistudio.baidu.com/llm/lmapi/v3", # aistudio 大模型 api 服务域名 ) chat_completion = client.chat.completions.create( model="ernie-4.5-turbo-32k", messages=[ { "role": "user", "content": "GPT-5发布会有哪些亮点?" } ], stream=True, extra_body={ "penalty_score": 1, "web_search": { "enable": True } }, max_completion_tokens=12288, temperature=0.95, top_p=0.7 ) for chunk in chat_completion: if hasattr(chunk.choices[0].delta, "reasoning_content") and chunk.choices[0].delta.reasoning_content: print(chunk.choices[0].delta.reasoning_content, end="", flush=True) else: print(chunk.choices[0].delta.content, end="", flush=True) ``` ##### 封装工具 ```python import erniebot erniebot.api_type = "aistudio" erniebot.access_token = os.environ.get("AISTUDIO_ACCESS_TOKEN") def nl_search(question:str): prompt = f""" 基于联网搜索结果回答此问题:{ question } 其他输出要求:答案中的关键信息必须标注精确到内容页面的来源链接 你的回答: """ response = erniebot.ChatCompletion.create( model="ernie-4.5", messages=[{ "role": "user", "content": prompt, }]) return response.get_result() ``` ##### 调用执行 ```python function_calling_request = ModelRequestWithFunctionCalling() ( function_calling_request .register_function( name="nl_search", description="使用此工具,可以用自然语言输入,获得基于网络搜索的事实性结果总结", parameters={ "type": "object", "properties": { "question": { "type": "string", "description": "使用自然语言总结用户关注的关键问题", } }, "required": ["question"], }, function=nl_search, ) ) question = "GPT-5发布会有哪些亮点?" result = function_calling_request.request( content=question, ) print(result) ``` ## 5. Function Calling在大模型应用场景中带来的“质变” - 知识层面:从模型自身知识(来源于训练语料)扩展到真实世界知识 - 行为层面:从“思考模拟器”、“问题应答”扩展到“理解问题-选择行动-发起请求-理解结果-给出回应” - 架构层面:让模型不再是一个孤立模块,而是可以融入现有信息系统之中 给软件开发思想带来的冲击: - 不是基于“规则”而是基于“世界理解”的调用 - 接纳没有明确的处理过程带来的输出不确定性(如数据查询) - 不走极端:“全盘拒绝”和“全盘接受”都不可取 ## 6. 智能体/LLM应用的定义 - Agent智能体的概念存在“过度炒作“的现象,部分媒体使用“智能体“这个词指代任何基于LLM能力构建的应用 - 不给出清晰定义的概念讨论甚至衍生讨论都是耍流氓 ### 6.1 机器学习概念中的Agent 在机器学习领域,智能体(Agent)通常指能够感知环境、做出决策并采取行动以实现特定目标的实体。这些智能体具备自主性,能够通过传感器获取环境信息,经过内部处理后,通过执行器对环境施加影响。这种架构使智能体能够在复杂、多变的环境中自主运作。 - 例如: - Alpha Go - 星际争霸/Dota 2对战AI - 学踢足球的AI [点击观看](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV11e4y1V7US/?share_source=copy_web&vd_source=b44770b90404f8e657d344a39ac5f758) ### 6.2 由各类开源项目实践并由Lilian Weng总结的LLM-Powered Autonomous Agents - 原文地址:https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/ - 重要意义:给基于LLM驱动的智能体讨论提供了共识性的基础定义 - 架构图: 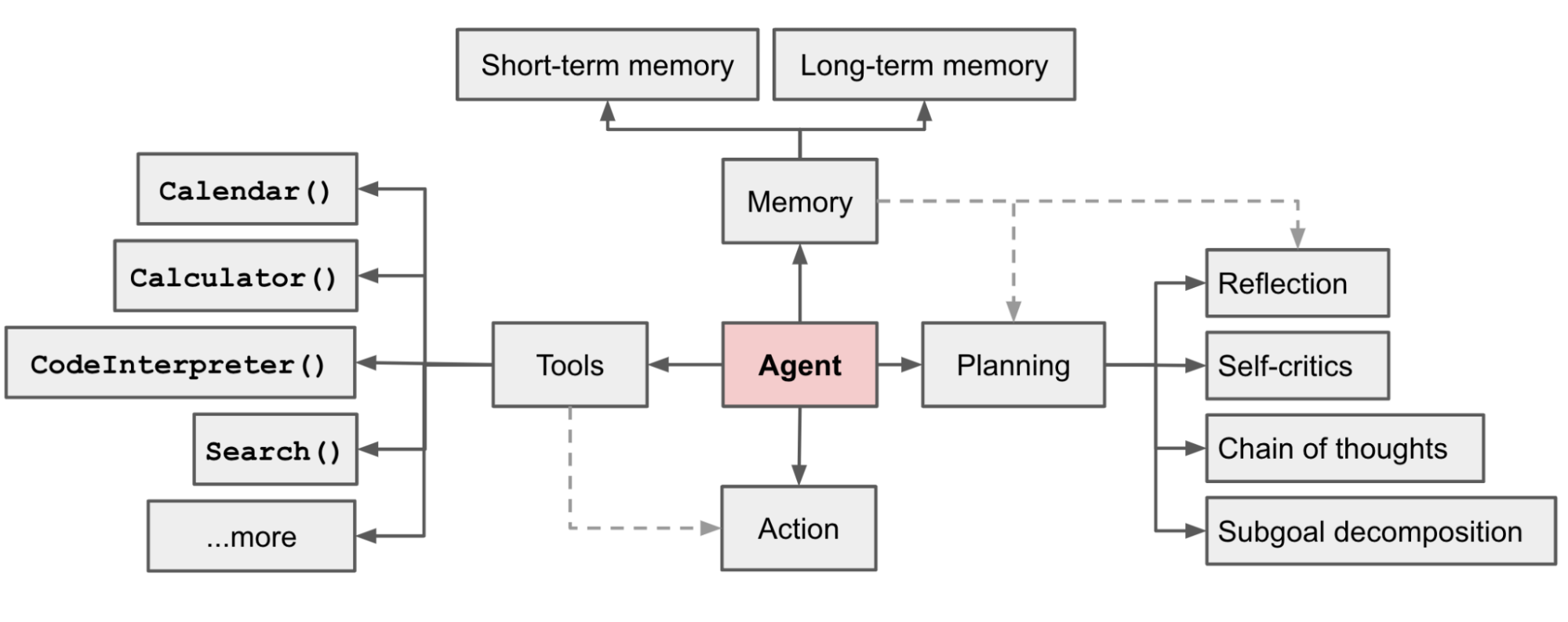 - 核心概念: - 核心驱动:LLM(提供基础智力、通识、逻辑、上下文内学习等基础能力) - 关键组件: - **规划(Planning)**:将复杂任务分解为可管理的子目标(Task Decomposition),并通过自我反思(Self-Reflection)来提高结果质量 - **记忆(Memory)**:包括短期记忆(对话记录)和<u>长期记忆(通过外部向量存储和快速检索来保留和回忆信息)</u>(这部分突破项目不多,去年有一个叫Mem0的项目刷过一次屏) - **工具使用(Tool Use)**:学习调用外部工具,补充额外信息或完成环境交互 - Inspiration: - [ReAct论文](https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.03629) - [AutoGPT](https://github.com/Significant-Gravitas/Auto-GPT) - [GPT-Engineer](https://github.com/AntonOsika/gpt-engineer) - [BabyAGI](https://github.com/yoheinakajima/babyagi) ### 6.3 多智能体协同 - 智能体概念的提出让一批使用类似上述结构(通常是简化的结构,比如只使用Role设定,或是ReAct Prompt)尝试进行多次模型请求协同的项目被关注,核心思想是通过不同的智能体分工协作,组成更大的协作网络 - 代表项目: - Camel.ai - MetaGPT - Microsoft AutoGen - OpenAI Swarm(现在的Agent SDK) ## 7. 智能体开发框架smolagents ### 7.1 smolagents 介绍 Github:https://github.com/huggingface/smolagents 官方文档:https://huggingface.co/docs/smolagents/index smolagents是HuggingFace官方推出的Agent开发库,构建强大 agent 的最简单框架!。 首先来介绍一下smolagents吧,smol是small的俏皮用法,故smolagents的含义是“轻量的agent工具”。smolagents库提供: ✨ **简洁性**:Agent 逻辑仅需约千行代码。我们将抽象保持在原始代码之上的最小形态! 🌐 **支持任何 LLM**:支持通过 Hub 托管的模型,使用其 `transformers` 版本或通过我们的推理 API 加载,也支持 OpenAI、Anthropic 等模型。使用任何 LLM 为 agent 提供动力都非常容易。 🧑💻 **一流的代码 agent 支持**,即编写代码作为其操作的 agent(与"用于编写代码的 agent"相对),[在此了解更多](tutorials/secure_code_execution)。 🤗 **Hub 集成**:您可以在 Hub 上共享和加载工具,更多功能即将推出! ## 8 实战:Agentic RAG ### 8.1 传统 RAG 的局限性 尽管传统 RAG 方法有诸多优势,但它也面临一些挑战: 1. 单次检索步骤:如果初始检索结果较差,则最终生成的结果将受到影响 2. 查询文档不匹配:用户查询(通常是问题)可能与包含答案(通常是陈述)的文档不太匹配 3. 推理能力有限:简单的 RAG 流程无法进行多步推理或查询细化 4. 上下文窗口约束:检索到的文档必须适合模型的上下文窗口 ### 8.2 Agentic RAG 的主要优势 拥有检索工具的代理可以: 1. ✅制定优化查询:代理可以将用户问题转换为易于检索的查询 2. ✅执行多次检索:代理可以根据需要迭代检索信息 3. ✅对检索到的内容进行推理:代理可以从多个来源进行分析、综合并得出结论 4. ✅自我批评和改进:代理可以评估检索结果并调整其方法 这种方法自然地实现了先进的 RAG 技术: - Hypothetical Document Embedding (HyDE):代理不直接使用用户查询,而是制定检索优化查询 - Self-Query Refinement:代理可以分析初始结果,并使用细化查询执行后续检索 ### 8.3 构建 Agentic RAG 系统 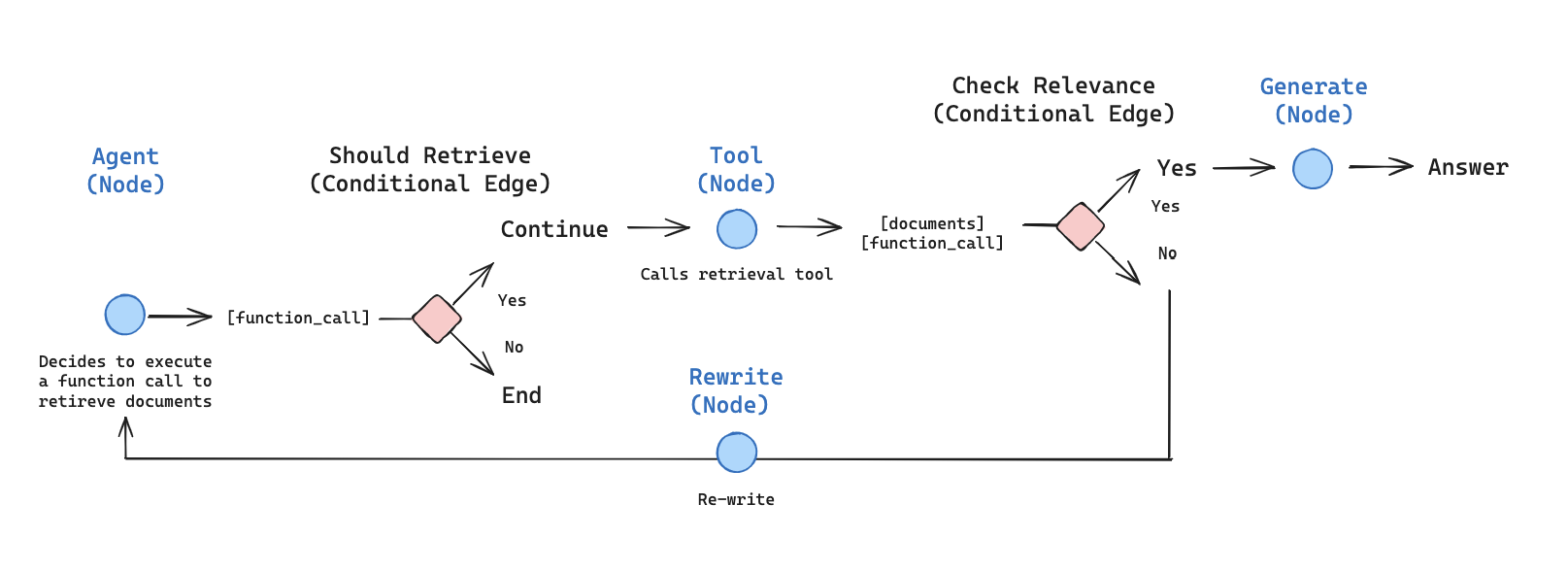 ```python # !pip install smolagents pandas langchain langchain-community sentence-transformers datasets rank_bm25 ``` 你需要一个有效的 token 作为环境变量 `HF_TOKEN` 来调用 Inference Providers。 Hugging Face 注册 - 登录 - 创建 Access Tokens - 系统环境变量配置 HF_TOKEN 我们首先加载一个知识库以在其上执行 RAG:此数据集是许多 Hugging Face 库的文档页面的汇编,存储为 markdown 格式。我们将仅保留 `transformers` 库的文档。然后通过处理数据集并将其存储到向量数据库中,为检索器准备知识库。我们将使用 [LangChain](https://python.langchain.com/docs/introduction/) 来利用其出色的向量数据库工具。 ```python import datasets from langchain.docstore.document import Document from langchain.text_splitter import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter from langchain_community.retrievers import BM25Retriever knowledge_base = datasets.load_dataset("m-ric/huggingface_doc", split="train") knowledge_base = knowledge_base.filter(lambda row: row["source"].startswith("huggingface/transformers")) source_docs = [ Document(page_content=doc["text"], metadata={"source": doc["source"].split("/")[1]}) for doc in knowledge_base ] text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter( chunk_size=500, chunk_overlap=50, add_start_index=True, strip_whitespace=True, separators=["\n\n", "\n", ".", " ", ""], ) docs_processed = text_splitter.split_documents(source_docs) ``` 现在文档已准备好。我们来一起构建我们的 agent RAG 系统! 👉 我们只需要一个 RetrieverTool,我们的 agent 可以利用它从知识库中检索信息。 由于我们需要将 vectordb 添加为工具的属性,我们不能简单地使用带有 `@tool` 装饰器的简单工具构造函数:因此我们将遵循 [tools 教程](../tutorials/tools) 中突出显示的高级设置。 ```python from smolagents import Tool class RetrieverTool(Tool): name = "retriever" description = "Uses semantic search to retrieve the parts of transformers documentation that could be most relevant to answer your query." inputs = { "query": { "type": "string", "description": "The query to perform. This should be semantically close to your target documents. Use the affirmative form rather than a question.", } } output_type = "string" def __init__(self, docs, **kwargs): super().__init__(**kwargs) self.retriever = BM25Retriever.from_documents( docs, k=10 ) def forward(self, query: str) -> str: assert isinstance(query, str), "Your search query must be a string" docs = self.retriever.invoke( query, ) return "\nRetrieved documents:\n" + "".join( [ f"\n\n===== Document {str(i)} =====\n" + doc.page_content for i, doc in enumerate(docs) ] ) retriever_tool = RetrieverTool(docs_processed) ``` BM25 检索方法是一个经典的检索方法,因为它的设置速度非常快。为了提高检索准确性,你可以使用语义搜索,使用文档的向量表示替换 BM25:因此你可以前往 [MTEB Leaderboard](https://huggingface.co/spaces/mteb/leaderboard) 选择一个好的嵌入模型。 现在我们已经创建了一个可以从知识库中检索信息的工具,现在我们可以很容易地创建一个利用这个 `retriever_tool` 的 agent!此 agent 将使用如下参数初始化: - `tools`:代理将能够调用的工具列表。 - `model`:为代理提供动力的 LLM。 我们的 `model` 必须是一个可调用对象,它接受一个消息的 list 作为输入,并返回文本。它还需要接受一个 stop_sequences 参数,指示何时停止生成。为了方便起见,我们直接使用包中提供的 `HfEngine` 类来获取调用 Hugging Face 的 Inference API 的 LLM 引擎。 接着,我们将使用 [meta-llama/Llama-3.3-70B-Instruct](meta-llama/Llama-3.3-70B-Instruct) 作为 llm 引 擎,因为: - 它有一个长 128k 上下文,这对处理长源文档很有用。 - 它在 HF 的 Inference API 上始终免费提供! _Note:_ 此 Inference API 托管基于各种标准的模型,部署的模型可能会在没有事先通知的情况下进行更新或替换。了解更多信息,请点击[这里](https://huggingface.co/docs/api-inference/supported-models)。 ```python from smolagents import InferenceClientModel, CodeAgent agent = CodeAgent( tools=[retriever_tool], model=InferenceClientModel(model_id="meta-llama/Llama-3.3-70B-Instruct"), max_steps=4 ) ``` 当我们初始化 CodeAgent 时,它已经自动获得了一个默认的系统提示,告诉 LLM 引擎按步骤处理并生成工具调用作为代码片段,但你可以根据需要替换此提示模板。接着,当其 `.run()` 方法被调用时,代理将负责调用 LLM 引擎,并在循环中执行工具调用,直到工具 `final_answer` 被调用,而其参数为最终答案。 ```python agent_output = agent.run("For a transformers model training, which is slower, the forward or the backward pass?") print("Final output:") print(agent_output) ``` ## 9. 智能体系统/LLM应用的应用场景 项目举例: - DeepResearch 应用场景举例: - 文案生成 - Auto Coder - NL2DB - 智能家居 - 智能座舱 ## 10. 智能体系统/LLM应用核心逻辑的几种分类 - CoT/简单工作流 - 附加Function Calling的单次请求 - 基于SOP的复杂工作流 - 自规划 - ... ## 11. 学习打卡 1. 掌握Function Calling核心概念和工作原理 2. 掌握智能体Agent核心概念和工作原理 3. 掌握智能体开发框架smolagents 4. 基于smolagents开发Agentic RAG应用,参考 smolagents\examples 目录下 `rag.py` 和 `rag_using_chromadb.py` 5. 基于smolagents开发text_to_sql应用,参考 smolagents\examples 目录下 `text_to_sql.py`
李智
2025年10月1日 11:47
转发文档
收藏文档
上一篇
下一篇
手机扫码
复制链接
手机扫一扫转发分享
复制链接
Markdown文件
分享
链接
类型
密码
更新密码