AI大模型学习
1、环境搭建
2、Embedding与向量数据库
3、RAG技术与应用
4、RAG高级技术与实践
5、LlamaIndex知识管理与信息检索
6、基于LlamaIndex开发的中医临床诊疗助手
7、LangChain多任务应用开发
8、Function Calling与Agent 智能体
9、Agent应用与图状态编排框架LangGraph
10、基于LangGraph实现智能分诊系统
11、MCP应用技术开发
12、AI 应用开发新范式 MCP 技术详解
13、基于LangGraph的多智能体交互系统
14、企业级智能分诊系统RAG项目
15、LangGraph与Agno-AGI深度对比分析
本文档使用 MrDoc 发布
-
+
首页
6、基于LlamaIndex开发的中医临床诊疗助手
# 中医临床智能诊疗助手 1. RAG 检索增强生成方案 2. Fine tuning 微调方案 ## 💡 学习后会带给你 1. 如何用你的垂域数据补充 LLM 的能力 2. 如何构建你的垂域(向量)知识库 3. 搭建一套完整 RAG 系统需要哪些模块 4. 搭建 RAG 系统时更多的有用技巧 5. 如何提升 RAG 检索的效果及优化实践 6. 生成级部署 RAG 系统方案 **学习目标:** 1. RAG 技术概述 2. RAG WorkFlow 及 RAG 工程化 3. 基于 LlamaIndex 快速构建 RAG 项目 4. 使用 LlamaIndex 存储和读取 Embedding 向量 5. 追踪哪些文档片段被用于检索增强生成 6. 深度剖析 RAG 检索底层实现细节 7. 自定义 RAG Prompt Template 8. RAG 项目企业级生产部署最佳实践 ## 一、 RAG 技术概述 ### 1.1 大模型目前固有的局限性 **大语言模型(LLM)是概率生成系统** - **知识时效性**:模型知识截止于训练数据时间点(**联网搜索**) - **推理局限性**:本质是概率预测而非逻辑运算,复杂数学推理易出错(**DeepSeek-R1的架构有所不同**) - **专业领域盲区**:缺乏垂直领域知识 - **幻觉现象**:可能生成看似合理但实际错误的内容 ### 1.2 什么是 RAG? RAG(Retrieval Augmented Generation)顾名思义,通过**检索**的方法来增强**生成模型**的能力。 ## 二、RAG 工程化 ### 2.1 RAG系统的基本搭建流程 搭建过程: 1. 文档加载,并按一定条件**切割**成片段 2. 将切割的文本片段灌入**检索引擎** 3. 封装**检索接口** 4. 构建**调用流程**:Query -> 检索 -> Prompt -> LLM -> 回复 ### 2.2 构建索引 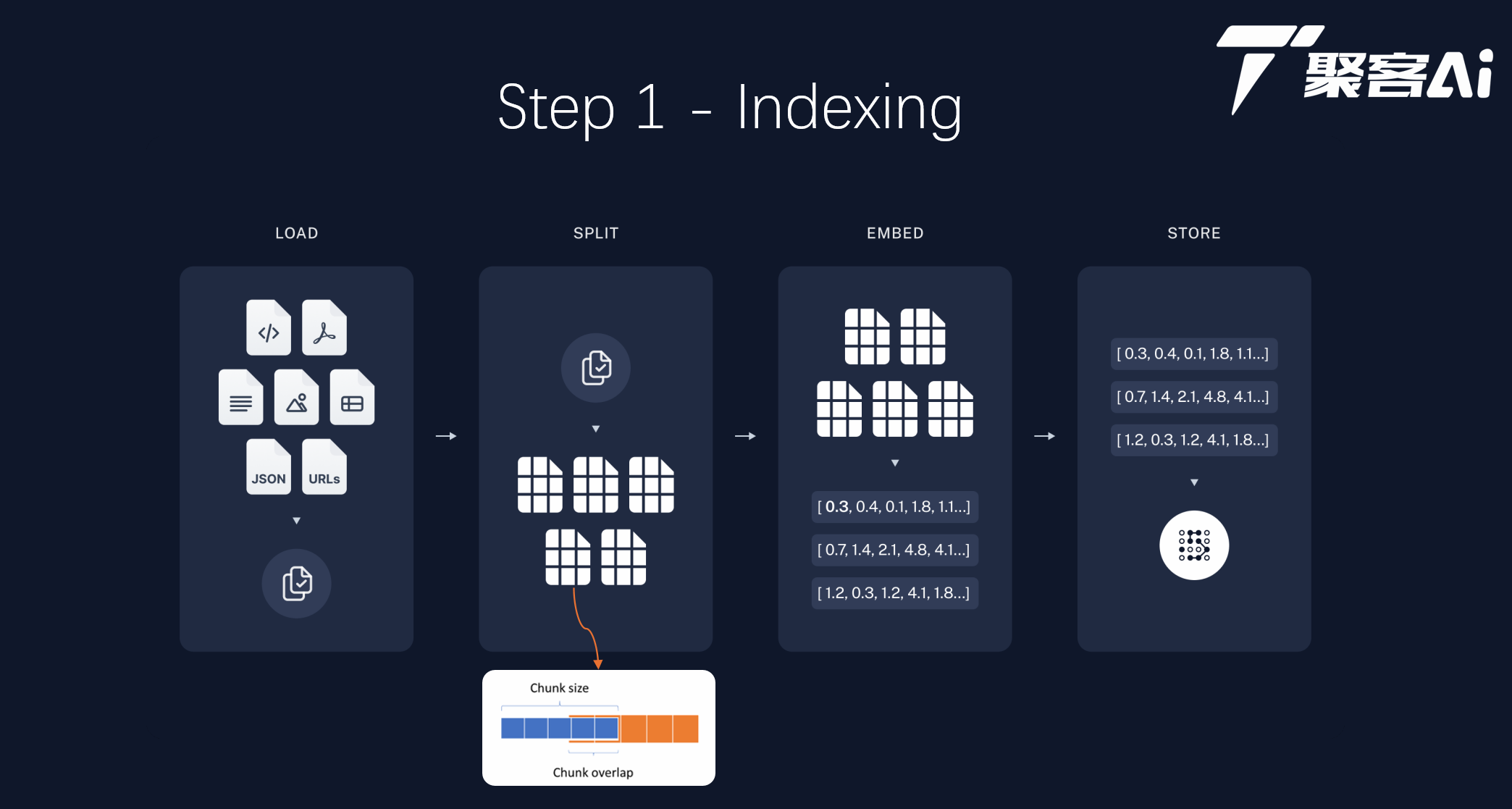 ### 2.3 检索和生成 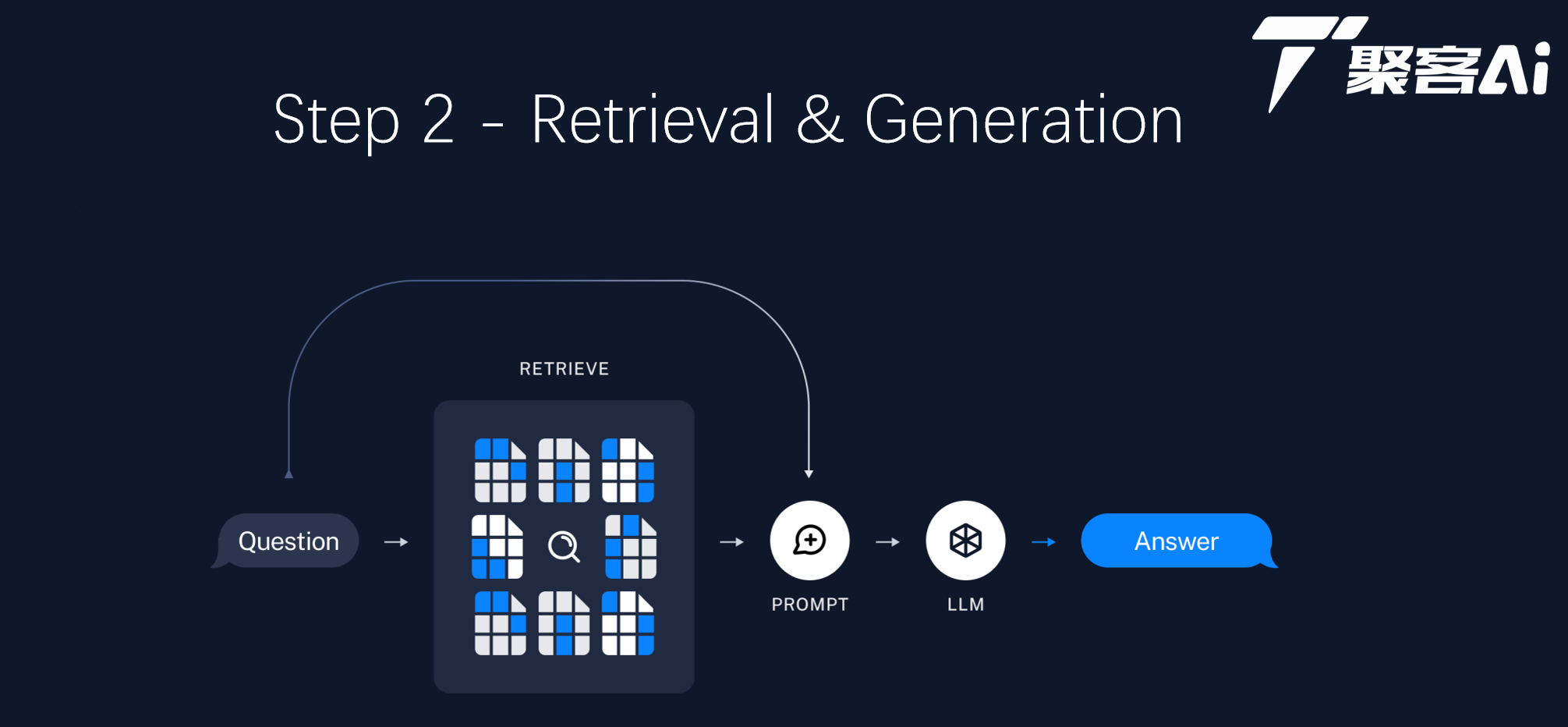 ## 三、项目环境配置 ### 3.1 使用 conda 创建项目环境 ```sh # 创建环境 conda create -n tcm-ai-rag python=3.11 # 激活环境 conda activate tcm-ai-rag ``` ### 3.2 安装项目所需依赖库 ```python # 安装 LlamaIndex 相关包 # !pip install llama-index # !pip install llama-index-embeddings-huggingface # !pip install llama-index-llms-huggingface ``` ```python # 安装 CUDA 版本 Pytorch # !pip install torch==2.5.1 torchvision==0.20.1 torchaudio==2.5.1 --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu124 ``` ## 四、模型下载 ```python # 安装 modelscope # !pip install modelscope ``` ### 4.1 下载 Embedding 模型权重 使用BAAI开源的中文bge模型作为embedding模型,使用modlescope提供的SDK将模型权重下载到本地服务器: ```python # 使用 modelscope 提供的 sdk 进行模型下载 from modelscope import snapshot_download # model_id 模型的id # cache_dir 缓存到本地的路径 model_dir = snapshot_download(model_id="BAAI/bge-base-zh-v1.5", cache_dir="/home/kevin/projects/models") ``` ### 4.2 下载 LLM 大模型权重 使用阿里开源的通义千问大模型,使用modelscope提供的SDK将模型权重下载到服务器: ```python # 使用 modelscope 提供的 sdk 进行模型下载 from modelscope import snapshot_download # model_id 模型的id # cache_dir 缓存到本地的路径 model_dir = snapshot_download(model_id="Qwen/Qwen1.5-7B-Chat", cache_dir="/home/kevin/projects/models") ``` ## 五、构建中医临床诊疗术语证候问答 ### 5.1 语料准备 本应用使用的文档是由国家卫生健康委员和国家中医药管理局发布的中医临床诊疗术语: - 《中医临床诊疗术语第1部分:疾病》(修订版).docx - 《中医临床诊疗术语第2部分:证候》(修订版).docx - 《中医临床诊疗术语第3部分:治法》(修订版).docx <div class="alert alert-danger"> <p><strong>需要对语料进行数据预处理,如去除噪声数据、数据格式化等</strong></p> <p>本文件中具有类目属性的术语一般不适用于临床诊断。</p> <p>注:类目属性的术语是指定义中有“泛指……一类证候”表述方式的术语。</p> </div> <div> <h3>部分内容展示:</h3> <p style="border:1px solid red;background:pink;padding:10px"> <span style="color:blue"><i>这种噪声数据就需要删除!</i></span><br> 4.1.1.2.1<br> 气机阻滞证 syndrome/pattern of obstructed qi movement<br> <strong>泛指因各种原因导致气机不畅,或气郁而不散,阻滞脏腑、经络、官窍等所引起的一类证候。</strong><br> </p> 4.1.1.2.1.1<br> **气机郁滞证 syndrome/pattern of qi activity stagnation**<br> 因气机郁结,阻滞经络或脏腑官窍所致。临床以头颈肩背或胸胁脘腹等处闷胀,或攻窜作痛,常随紧张、抑郁等情绪缓解,或得太息、嗳气、肠鸣、矢气而减轻,脉弦,可伴见大便时秘或泻,小便不利,耳鸣、耳聋,嘶哑、呃逆等为特征的证候。<br> 4.1.1.2.1.2<br> **气滞耳窍证 syndrome/pattern of qi stagnation in the ears**<br> 因肝气郁结,气机不利,气滞耳窍所致。临床以突然耳窍失聪,或耳内堵塞,耳鸣,眩晕,脉弦,伴见胸胁胀闷,情绪抑郁等为特征的证候。<br> 4.1.1.2.1.3<br> **气滞声带证 syndrome/pattern of qi stagnation in the vocal fold**<br> 因气机阻滞,痹阻声带所致。临床以声音不扬、嘶哑,言语费劲或磕巴,脉弦,可伴见咽喉不适,胸闷、胁胀等为特征的证候。<br> </div> - 删除文件中的英文和/ 代码: ```python import re def remove_english(input_file, output_file): """ 去除文件中所有英文字符并生成新文件 :param input_file: 输入文件路径 :param output_file: 输出文件路径 """ try: with open(input_file, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f_in: content = f_in.read() # 使用正则表达式移除所有英文字母 filtered_content = re.sub('[A-Za-z/]', '', content) with open(output_file, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f_out: f_out.write(filtered_content) print(f"处理完成,已生成新文件:{output_file}") except Exception as e: print(f"处理出错:{str(e)}") # 使用示例 # remove_english('./data/demo-2.txt', './data/demo-2-1.txt') ``` 处理完成,已生成新文件:./data/demo-2-1.txt ### 5.2 基于 LlamaIndex 来快速构建知识库 #### 5.2.1 导入所需的包 ```python import logging import sys import torch from llama_index.core import PromptTemplate, Settings, SimpleDirectoryReader, VectorStoreIndex, load_index_from_storage, StorageContext, QueryBundle from llama_index.core.schema import MetadataMode from llama_index.embeddings.huggingface import HuggingFaceEmbedding from llama_index.llms.huggingface import HuggingFaceLLM from llama_index.core.node_parser import SentenceSplitter ``` #### 5.2.2 定义日志配置 ```python logging.basicConfig(stream=sys.stdout, level=logging.INFO) logging.getLogger().addHandler(logging.StreamHandler(stream=sys.stdout)) ``` #### 5.2.3 定义 System Prompt ```python SYSTEM_PROMPT = """You are a helpful AI assistant.""" query_wrapper_prompt = PromptTemplate( "[INST]<<SYS>>\n" + SYSTEM_PROMPT + "<</SYS>>\n\n{query_str}[/INST] " ) ``` #### 5.2.4 使用 llama_index_llms_huggingface 调用本地大模型 ```python from transformers import BitsAndBytesConfig quantization_config = BitsAndBytesConfig( load_in_4bit = True, bnb_4bit_quant_type = "nf4", bnb_4bit_use_double_quant = True, # 启用嵌套量化,在第一轮量化之后会进行第二轮量化,为每个参数额外节省 0.4 比特 bnb_4bit_compute_dtype = torch.bfloat16, # 更改量化模型的计算数据类型来加速训练 ) Settings.llm = HuggingFaceLLM( context_window = 4096, max_new_tokens = 2048, generate_kwargs = {"temperature": 0.0, "do_sample": False}, query_wrapper_prompt = query_wrapper_prompt, tokenizer_name = "/home/kevin/projects/models/Qwen/Qwen1.5-7B-Chat", model_name = "/home/kevin/projects/models/Qwen/Qwen1.5-7B-Chat", device_map = "auto", #"auto","balanced","balanced_low_0","sequential" model_kwargs = { "trust_remote_code":True, "quantization_config": quantization_config } ) ``` <div class="alert alert-danger"> <p><strong>注意:为了输出的可复现性</strong></p> <ul> <li>将大模型的temperature设置为0,do_sample设置为False,所以两次得到的输出基本相同;</li> <li>如果将temperature设置为大于0的小数,do_sample设置为True,大模型每次的输出可能都是不一样的。</li> <li>另外,如果你在实验时获得的输出与文中的输出不一致,这也是正常的,这与多个因素有关。</li> </ul> </div> #### 5.2.5 使用 llama_index_embeddings_huggingface 调用本地 embedding 模型 ```python Settings.embed_model = HuggingFaceEmbedding( model_name="/home/kevin/projects/models/BAAI/bge-base-zh-v1.5" ) ``` #### 5.2.6 读取文档 ```python documents = SimpleDirectoryReader("./data", required_exts=[".txt"]).load_data() ``` #### 5.2.7 对文档进行切分,将切分后的片段转化为embedding向量,构建向量索引 ```python index = VectorStoreIndex.from_documents(documents, transformations=[SentenceSplitter(chunk_size=256)]) ``` SentenceSplitter 参数详细设置: 预设会以 1024 个 token 为界切割片段, 每个片段的开头重叠上一个片段的 200 个 token 的内容。 ```properties chunk_size = 1024, # 切片 token 数限制 chunk_overlap = 200, # 切片开头与前一片段尾端的重复 token 数 paragraph_separator = '\n\n\n', # 段落的分界 secondary_chunking_regex = '[^,.;。?!]+[,.;。?!]?' # 单一句子的样式 separator = ' ', # 最小切割的分界字元 ``` #### 5.2.8 构建查询引擎 ```python # streaming 流式输出 # similarity_top_k 检索结果的数量 query_engine = index.as_query_engine(streaming=True, similarity_top_k=5) ``` #### 5.2.9 生成答案 ```python response = query_engine.query("不耐疲劳,口燥、咽干可能是哪些证候?") response.print_response_stream() print() ``` 从提供的信息来看,不耐疲劳、口燥、咽干等症状可能与以下几种证候相关: 1. **津液不足证 (Syndrome of Fluid and Humor Insufficiency)**:这种证候的特点是口眼喉鼻及皮肤等部位干燥,大便干结,小便短少,舌质偏红而干,脉细数。这些症状与不耐疲劳、口燥、咽干相符。 2. **津液亏涸证 (Syndrome of Fluid and Humor Scantiness)**:这种证候表现为口干、唇裂,鼻燥无涕,皮肤干瘪,目陷、螺瘪,甚则肌肤甲错,舌质红而少津,舌中裂,脉细或数。这些症状也包括口燥和咽干。 3. **燥邪犯肺证 (Syndrome of Pathogenic Dryness Invading the Lung)**:这种证候的特点是干咳、少痰或无痰,痰黏不易咳出,唇鼻咽喉干燥,声音嘶哑,口渴,咳甚则胸痛,或痰中血丝,舌尖红,舌苔薄黄、少津,脉细或数。其中唇鼻咽喉干燥的症状与口燥、咽干相符。 4. **燥干清窍证 (Syndrome of Dryness Harassing the Upper Orifices)**:这种证候的特点是口鼻、咽喉干燥,两眼干涩,少泪、少涕、少津、甚则衄血,舌质瘦小、舌苔干而少津,脉细。这些症状也包括口燥、咽干。 综上所述,不耐疲劳、口燥、咽干等症状可能与津液不足证、津液亏涸证、燥邪犯肺证以及燥干清窍证相关。具体诊断需要结合其他临床表现和舌脉象综合判断。 ## 六、使用LlamaIndex存储和读取embedding向量 ### 6.1 上面面临的问题 - 使用llama-index-llms-huggingface构建本地大模型时,会花费相当一部分时间 - 在对文档进行切分,将切分后的片段转化为embedding向量,构建向量索引时,会花费大量的时间 ### 6.2 向量存储 ```python # 将embedding向量和向量索引存储到文件中 # ./doc_emb 是存储路径 index.storage_context.persist(persist_dir='./doc_emb') ``` 找到刚才定义的persist_dir所在的路径,可以发现该路径下有以下几个文件: - **default_vector_store.json**:用于存储embedding向量 - **docstore.json**:用于存储文档切分出来的片段 - graph_store.json:用于存储知识图数据 - image__vector_store.json:用于存储图像数据 - **index_store.json**:用于存储向量索引 在上述代码中,我们只用到了纯文本文档,所以生成出来的`graph_store.json`和`image__vector_store.json`中没有数据。 #### 6.3 从向量数据库检索 将embedding向量和向量索引存储到文件中后,我们就不需要重复地执行对文档进行切分,将切分后的片段转化为embedding向量,构建向量索引的操作了。 以下代码演示了如何使用LlamaIndex读取结构化文件中的embedding向量和向量索引数据: ```python # 从存储文件中读取embedding向量和向量索引 storage_context = StorageContext.from_defaults(persist_dir="./doc_emb") # 根据存储的embedding向量和向量索引重新构建检索索引 index = load_index_from_storage(storage_context) # 构建查询引擎 query_engine = index.as_query_engine(streaming=True, similarity_top_k=5) # 查询获得答案 response = query_engine.query("不耐疲劳,口燥、咽干可能是哪些证候?") response.print_response_stream() print() ``` 从提供的信息来看,不耐疲劳、口燥、咽干等症状可能与以下几种证候相关: 1. **津液不足证 (Syndrome of Fluid and Humor Insufficiency)**:这种证候的特点是口眼喉鼻及皮肤等部位干燥,大便干结,小便短少,舌质偏红而干,脉细数。这些症状与不耐疲劳、口燥、咽干相符。 2. **津液亏涸证 (Syndrome of Fluid and Humor Scantiness)**:这种证候表现为口干、唇裂,鼻燥无涕,皮肤干瘪,目陷、螺瘪,甚则肌肤甲错,舌质红而少津,舌中裂,脉细或数。这些症状也包括口燥和咽干。 3. **燥邪犯肺证 (Syndrome of Pathogenic Dryness Invading the Lung)**:这种证候的特点是干咳、少痰或无痰,痰黏不易咳出,唇鼻咽喉干燥,声音嘶哑,口渴,咳甚则胸痛,或痰中血丝,舌尖红,舌苔薄黄、少津,脉细或数。其中唇鼻咽喉干燥的症状与口燥、咽干相符。 4. **燥干清窍证 (Syndrome of Dryness Harassing the Upper Orifices)**:这种证候的特点是口鼻、咽喉干燥,两眼干涩,少泪、少涕、少津、甚则衄血,舌质瘦小、舌苔干而少津,脉细。这些症状也包括口燥、咽干。 综上所述,不耐疲劳、口燥、咽干等症状可能与津液不足证、津液亏涸证、燥邪犯肺证以及燥干清窍证相关。具体诊断需要结合其他临床表现和舌脉象综合判断。 ## 七、追踪哪些文档片段被检索 ```python # 从存储文件中读取embedding向量和向量索引 storage_context = StorageContext.from_defaults(persist_dir="./doc_emb") # 根据存储的embedding向量和向量索引重新构建检索索引 index = load_index_from_storage(storage_context) # 构建查询引擎 query_engine = index.as_query_engine(similarity_top_k=5) # 获取我们抽取出的相似度 top 5 的片段 contexts = query_engine.retrieve(QueryBundle("不耐疲劳,口燥、咽干可能是哪些证候?")) print('-' * 10 + 'ref' + '-' * 10) for i, context in enumerate(contexts): print('#' * 10 + f'chunk {i} start' + '#' * 10) content = context.node.get_content(metadata_mode=MetadataMode.LLM) print(content) print('#' * 10 + f'chunk {i} end' + '#' * 10) print('-' * 10 + 'ref' + '-' * 10) # 查询获得答案 response = query_engine.query("不耐疲劳,口燥、咽干可能是哪些证候?") print(response) ``` 追踪结果: ```python ----------ref---------- ##########chunk 0 start########## file_path: /home/jukeai/ai_projects/tcm-ai-rag/documents/demo-1.txt 临床以口眼喉鼻及皮肤等干燥,大便干结,小便短少,舌质偏红而干,脉细数等为特征的证候。 4.6.1.2 津液亏涸证 syndrome/pattern of fluid and humor scantiness 津液亏耗证 津液干枯证 因津液亏损,形体官窍失养所致。临床以口干、唇裂,鼻燥无涕,皮肤干瘪,目陷、螺瘪,甚则肌肤甲错,舌质红而少津,舌中裂,脉细或数,可伴见口渴、欲饮,干咳,目涩,大便干,小便少等为特征的证候。 ##########chunk 0 end########## ##########chunk 1 start########## file_path: /home/jukeai/ai_projects/tcm-ai-rag/documents/demo-1.txt 临床以口干、舌燥,频饮而不解其渴,食多、善饥,夜尿频多,逐渐消瘦,舌质红,舌苔薄黄或少,脉弦细或滑数,伴见皮肤干燥,四肢乏力,大便干结等为特征的证候。 4.6.3.2 津亏热结证 syndrome/pattern of fluid depletion and heat binding 液干热结证 因津液亏虚,热邪内结所致。 ##########chunk 1 end########## ##########chunk 2 start########## file_path: /home/jukeai/ai_projects/tcm-ai-rag/documents/demo-1.txt 临床以口鼻、咽喉干燥,两眼干涩,少泪、少涕、少津、甚则衄血,舌质瘦小、舌苔干而少津,脉细等为特征的证候。 3.6.3.3 燥邪犯肺证 syndrome/pattern of pathogenic dryness invading the lung 燥邪伤肺证 因外感燥邪,或感受风热,化燥伤阴,肺失清肃所致。临床以干咳、少痰或无痰,痰黏不易咳出,唇鼻咽喉干燥,声音嘶哑,口渴,咳甚则胸痛,或痰中血丝,舌尖红,舌苔薄黄、少津,脉细或数,初起或伴见发热、恶寒,头痛等为特征的证候。 ##########chunk 2 end########## ##########chunk 3 start########## file_path: /home/jukeai/ai_projects/tcm-ai-rag/documents/demo-1.txt 临床以鼻咽干涩或痛,口唇燥干,舌质红,舌苔白或燥,脉浮或微数,伴见发热、无汗,头痛或肢节酸痛等为特征的证候。 3.6.3.2 燥干清窍证 syndrome/pattern of dryness harassing the upper orifices 因气候或环境干燥,津液耗损,清窍失濡所致。临床以口鼻、咽喉干燥,两眼干涩,少泪、少涕、少津、甚则衄血,舌质瘦小、舌苔干而少津,脉细等为特征的证候。 ##########chunk 3 end########## ##########chunk 4 start########## file_path: /home/jukeai/ai_projects/tcm-ai-rag/documents/demo-1.txt 4.6.1.1 津液不足证 syndrome/pattern of fluid and humor insufficiency 津亏证 因津液生成不足,或嗜食辛辣,蕴热化燥,邪热灼损津液所致。临床以口眼喉鼻及皮肤等干燥,大便干结,小便短少,舌质偏红而干,脉细数等为特征的证候。 ##########chunk 4 end########## ----------ref---------- ``` <div class="alert alert-info"> <ul> <li>追踪检索片段,调整chunk_size的值,可以让embedding模型切分出的片段更合理,提高RAG系统的表现。 <li>如果想追踪更多的检索片段,可以提高 similarity_top_k 的值。</li> <li>如果想追踪片段具体的相似度得分(Similarity Score)的值,可以将log中的level设置为DEBUG级别。</li> </ul> </div> ## 八、RAG 检索底层实现细节 知道了如何追踪哪些文档片段被用于检索增强生成,但我们仍不知道RAG过程中到底发生了什么,为什么大模型能够根据检索出的文档片段进行回复? ```python import logging import sys import torch from llama_index.core import PromptTemplate, Settings, StorageContext, load_index_from_storage from llama_index.core.callbacks import LlamaDebugHandler, CallbackManager from llama_index.embeddings.huggingface import HuggingFaceEmbedding from llama_index.llms.huggingface import HuggingFaceLLM # 定义日志 logging.basicConfig(stream=sys.stdout, level=logging.DEBUG) logging.getLogger().addHandler(logging.StreamHandler(stream=sys.stdout)) # 定义system prompt SYSTEM_PROMPT = """You are a helpful AI assistant.""" query_wrapper_prompt = PromptTemplate( "[INST]<<SYS>>\n" + SYSTEM_PROMPT + "<</SYS>>\n\n{query_str}[/INST] " ) # 使用llama-index创建本地大模型 Settings.llm = HuggingFaceLLM( context_window = 4096, max_new_tokens = 2048, generate_kwargs = {"temperature": 0.0, "do_sample": False}, query_wrapper_prompt = query_wrapper_prompt, tokenizer_name = "/home/kevin/projects/models/Qwen/Qwen1.5-7B-Chat", model_name = "/home/kevin/projects/models/Qwen/Qwen1.5-7B-Chat", device_map = "auto", model_kwargs = {"torch_dtype": torch.float16}, ) # 使用LlamaDebugHandler构建事件回溯器,以追踪LlamaIndex执行过程中发生的事件 llama_debug = LlamaDebugHandler(print_trace_on_end=True) callback_manager = CallbackManager([llama_debug]) Settings.callback_manager = callback_manager # 使用llama-index-embeddings-huggingface构建本地embedding模型 Settings.embed_model = HuggingFaceEmbedding( model_name = "/home/kevin/projects/models/BAAI/bge-base-zh-v1.5" ) # 从存储文件中读取embedding向量和向量索引 storage_context = StorageContext.from_defaults(persist_dir="./doc_emb") # 根据存储的embedding向量和向量索引重新构建检索索引 index = load_index_from_storage(storage_context) # 构建查询引擎 query_engine = index.as_query_engine(similarity_top_k=5) # 查询获得答案 response = query_engine.query("不耐疲劳,口燥、咽干可能是哪些证候?") print(response) # get_llm_inputs_outputs 返回每个LLM调用的开始/结束事件 event_pairs = llama_debug.get_llm_inputs_outputs() # print(event_pairs[0][1].payload.keys()) # 输出事件结束时所有相关的属性 # 输出 Promt 构建过程 print(event_pairs[0][1].payload["formatted_prompt"]) ``` ### 8.1 Query 过程分析 <pre> ********** Trace: query |_query -> 63.648696 seconds |_retrieve -> 1.186543 seconds |_embedding -> 1.047233 seconds |_synthesize -> 62.461404 seconds |_templating -> 3.3e-05 seconds |_llm -> 62.451146 seconds ********** </pre> 以上的输出记录了query在程序过程中经历的阶段和所用的时间,整个过程分为两个阶段: - 抽取(retrieve) - 合成(synthesize)。 合成阶段的templating步骤会将query和抽取出来的文档片段组合成模板,构成新的query,然后调用LLM,得到最终的response。 所以,只要找到templating所构建的新query,就可以知道为什么大模型能够根据我们检索出来的文档进行回复了。 ### 8.2 formatted_prompt 下面这段文本就是 print(event_pairs[0][1].payload["formatted_prompt"]) 语句输出的, 下面这段文本就是 `templating` 后的新 `query` 原始query由"不耐疲劳,口燥、咽干可能是哪些证候?"变成了下面这段很长的新query,由于我们给大模型提供了一些文档片段知识,并且要求大模型根据提供的检索知识回答原始query,因此大模型能够根据检索出的文档片段进行回复。(这其实也就是RAG技术的本质了) ```python [INST]<<SYS>> You are a helpful AI assistant.<</SYS>> Context information is below. --------------------- file_path: /home/jukeai/ai_projects/tcm-ai-rag/documents/demo-1.txt 临床以口眼喉鼻及皮肤等干燥,大便干结,小便短少,舌质偏红而干,脉细数等为特征的证候。 4.6.1.2 津液亏涸证 syndrome/pattern of fluid and humor scantiness 津液亏耗证 津液干枯证 因津液亏损,形体官窍失养所致。临床以口干、唇裂,鼻燥无涕,皮肤干瘪,目陷、螺瘪,甚则肌肤甲错,舌质红而少津,舌中裂,脉细或数,可伴见口渴、欲饮,干咳,目涩,大便干,小便少等为特征的证候。 file_path: /home/jukeai/ai_projects/tcm-ai-rag/documents/demo-1.txt 临床以口干、舌燥,频饮而不解其渴,食多、善饥,夜尿频多,逐渐消瘦,舌质红,舌苔薄黄或少,脉弦细或滑数,伴见皮肤干燥,四肢乏力,大便干结等为特征的证候。 4.6.3.2 津亏热结证 syndrome/pattern of fluid depletion and heat binding 液干热结证 因津液亏虚,热邪内结所致。 file_path: /home/jukeai/ai_projects/tcm-ai-rag/documents/demo-1.txt 临床以口鼻、咽喉干燥,两眼干涩,少泪、少涕、少津、甚则衄血,舌质瘦小、舌苔干而少津,脉细等为特征的证候。 3.6.3.3 燥邪犯肺证 syndrome/pattern of pathogenic dryness invading the lung 燥邪伤肺证 因外感燥邪,或感受风热,化燥伤阴,肺失清肃所致。临床以干咳、少痰或无痰,痰黏不易咳出,唇鼻咽喉干燥,声音嘶哑,口渴,咳甚则胸痛,或痰中血丝,舌尖红,舌苔薄黄、少津,脉细或数,初起或伴见发热、恶寒,头痛等为特征的证候。 file_path: /home/jukeai/ai_projects/tcm-ai-rag/documents/demo-1.txt 临床以鼻咽干涩或痛,口唇燥干,舌质红,舌苔白或燥,脉浮或微数,伴见发热、无汗,头痛或肢节酸痛等为特征的证候。 3.6.3.2 燥干清窍证 syndrome/pattern of dryness harassing the upper orifices 因气候或环境干燥,津液耗损,清窍失濡所致。临床以口鼻、咽喉干燥,两眼干涩,少泪、少涕、少津、甚则衄血,舌质瘦小、舌苔干而少津,脉细等为特征的证候。 file_path: /home/jukeai/ai_projects/tcm-ai-rag/documents/demo-1.txt 4.6.1.1 津液不足证 syndrome/pattern of fluid and humor insufficiency 津亏证 因津液生成不足,或嗜食辛辣,蕴热化燥,邪热灼损津液所致。临床以口眼喉鼻及皮肤等干燥,大便干结,小便短少,舌质偏红而干,脉细数等为特征的证候。 4.6.1. --------------------- Given the context information and not prior knowledge, answer the query. Query: 不耐疲劳,口燥、咽干可能是哪些证候? Answer: [/INST] ``` <div class="alert alert-warning"> <ul> <li>新query中既有中文,也有英文,这是因为LlamaIndex框架默认构建的模板都是英文的</li> <li>LlamaIndex允许自定义查询流程,构建自己的中文模板</li> </ul> </div> ### 8.3 Retrieve 检索进阶 抽取(retrieve)阶段的retrievers模块规定了针对查询从知识库获取相关上下文的技术。我们之前使用的都是默认的方法,其实LlamaIndex官方为我们提供了一些其他常用的方法: - SimilarityPostprocessor: 使用similarity_cutoff设置阈值。移除低于某个相似度分数的节点。 - KeywordNodePostprocessor: 使用required_keywords和exclude_keywords。根据关键字包含或排除过滤节点。 - MetadataReplacementPostProcessor: 用其元数据中的数据替换节点内容。 - LongContextReorder: 重新排序节点,这有利于需要大量顶级结果的情况,可以解决模型在扩展上下文中的困难。 - SentenceEmbeddingOptimizer: 选择percentile_cutoff或threshold_cutoff作为相关性。基于嵌入删除不相关的句子。 - CohereRerank: 使用coherence ReRank对节点重新排序,返回前N个结果。 - SentenceTransformerRerank: 使用SentenceTransformer交叉编码器对节点重新排序,产生前N个节点。 - LLMRerank: 使用LLM对节点重新排序,为每个节点提供相关性评分。 - FixedRecencyPostprocessor: 返回按日期排序的节点。 - EmbeddingRecencyPostprocessor: 按日期对节点进行排序,但也会根据嵌入相似度删除较旧的相似节点。 - TimeWeightedPostprocessor: 对节点重新排序,偏向于最近未返回的信息。 - PIINodePostprocessor(β): 可以利用本地LLM或NER模型删除个人身份信息。 - PrevNextNodePostprocessor(β): 根据节点关系,按顺序检索在节点之前、之后或两者同时出现的节点 ### 8.4 响应合成器 response synthesizer 合成(synthesize)阶段的响应合成器(response synthesizer)会引导LLM生成响应,将用户查询与检索到的文本块混合在一起,并给出一个精心设计的答案。 LlamaIndex官方为我们提供了多种响应合成器: - Refine: 这种方法遍历每一段文本,一点一点地精炼答案。 - Compact: 是Refine的精简版。它将文本集中在一起,因此需要处理的步骤更少。 - Tree Summarize: 想象一下,把许多小的答案结合起来,再总结,直到你得到一个主要的答案。 - Simple Summarize: 只是把文本片段剪短,然后给出一个快速的总结。 - No Text: 这个问题不会给你答案,但会告诉你它会使用哪些文本。 - Accumulate: 为每一篇文章找一堆小答案,然后把它们粘在一起。 - Compact Accumulate: 是“Compact”和“Accumulate”的合成词。 现在,我们选择一种retriever和一种response synthesizer。retriever选择SimilarityPostprocessor,response synthesizer选择Refine。 ```python import logging import sys import torch from llama_index.core import PromptTemplate, Settings, SimpleDirectoryReader, VectorStoreIndex, get_response_synthesizer from llama_index.core.callbacks import LlamaDebugHandler, CallbackManager from llama_index.core.indices.vector_store import VectorIndexRetriever from llama_index.core.postprocessor import SimilarityPostprocessor from llama_index.core.query_engine import RetrieverQueryEngine from llama_index.core.response_synthesizers import ResponseMode from llama_index.embeddings.huggingface import HuggingFaceEmbedding from llama_index.llms.huggingface import HuggingFaceLLM # 定义日志 logging.basicConfig(stream=sys.stdout, level=logging.INFO) logging.getLogger().addHandler(logging.StreamHandler(stream=sys.stdout)) # 定义system prompt SYSTEM_PROMPT = """You are a helpful AI assistant.""" query_wrapper_prompt = PromptTemplate( "[INST]<<SYS>>\n" + SYSTEM_PROMPT + "<</SYS>>\n\n{query_str}[/INST] " ) # 使用 llama_index_llms_huggingface 调用本地大模型 Settings.llm = HuggingFaceLLM( context_window = 4096, max_new_tokens = 2048, generate_kwargs = {"temperature": 0.0, "do_sample": False}, query_wrapper_prompt = query_wrapper_prompt, tokenizer_name = "/home/kevin/projects/models/Qwen/Qwen1.5-7B-Chat", model_name = "/home/kevin/projects/models/Qwen/Qwen1.5-7B-Chat", device_map = "auto", model_kwargs = {"torch_dtype": torch.float16}, ) # 使用LlamaDebugHandler构建事件回溯器,以追踪LlamaIndex执行过程中发生的事件 llama_debug = LlamaDebugHandler(print_trace_on_end=True) callback_manager = CallbackManager([llama_debug]) Settings.callback_manager = callback_manager # 使用llama-index-embeddings-huggingface构建本地embedding模型 Settings.embed_model = HuggingFaceEmbedding( model_name="/home/kevin/projects/models/BAAI/bge-base-zh-v1.5" ) # 读取文档并构建索引 documents = SimpleDirectoryReader("./data").load_data() index = VectorStoreIndex.from_documents(documents) # 构建retriever retriever = VectorIndexRetriever( index = index, similarity_top_k = 5, ) # 构建response synthesizer response_synthesizer = get_response_synthesizer( response_mode = ResponseMode.REFINE ) # 构建查询引擎 query_engine = RetrieverQueryEngine( retriever = retriever, response_synthesizer = response_synthesizer, node_postprocessors = [SimilarityPostprocessor(similarity_cutoff=0.6)] ) # 查询获得答案 response = query_engine.query("不耐疲劳,口燥、咽干可能是哪些证候?") print(response) # get_llm_inputs_outputs返回每个LLM调用的开始/结束事件 event_pairs = llama_debug.get_llm_inputs_outputs() print(event_pairs[0][1].payload["formatted_prompt"]) ``` <pre> ********** Trace: query |_query -> 61.077074 seconds |_synthesize -> 61.03387 seconds |_templating -> 2.3e-05 seconds |_llm -> 5.93741 seconds |_templating -> 2.2e-05 seconds |_llm -> 6.627645 seconds |_templating -> 2.3e-05 seconds |_llm -> 13.074158 seconds |_templating -> 2.5e-05 seconds |_llm -> 9.181957 seconds |_templating -> 2.3e-05 seconds |_llm -> 26.191079 seconds ********** </pre> 可以看出,将response synthesizer由默认的Compact替换为Refine之后,query在程序过程中经历的阶段发生了变化,REFINE模式会进行更多次的templating和LLM调用。 实际开发中可以自由组合不同的retriever和response synthesizer,以完成我们的需求。当LlamaIndex提供的retriever和response synthesizer不能满足我们的需求的时候,我们还可以自定义retriever和response synthesizer。 ## 九、自定义 Prompt LlamaIndex中提供的prompt template都是英文的,该如何使用中文的prompt template呢? ```python import logging import sys import torch from llama_index.core import PromptTemplate, Settings, StorageContext, load_index_from_storage from llama_index.core.callbacks import LlamaDebugHandler, CallbackManager from llama_index.embeddings.huggingface import HuggingFaceEmbedding from llama_index.llms.huggingface import HuggingFaceLLM # 定义日志 logging.basicConfig(stream=sys.stdout, level=logging.INFO) logging.getLogger().addHandler(logging.StreamHandler(stream=sys.stdout)) # 定义system prompt SYSTEM_PROMPT = """你是一个医疗人工智能助手。""" query_wrapper_prompt = PromptTemplate( "[INST]<<SYS>>\n" + SYSTEM_PROMPT + "<</SYS>>\n\n{query_str}[/INST] " ) # 定义qa prompt qa_prompt_tmpl_str = ( "上下文信息如下。\n" "---------------------\n" "{context_str}\n" "---------------------\n" "请根据上下文信息而不是先验知识来回答以下的查询。" "作为一个医疗人工智能助手,你的回答要尽可能严谨。\n" "Query: {query_str}\n" "Answer: " ) qa_prompt_tmpl = PromptTemplate(qa_prompt_tmpl_str) # 定义refine prompt refine_prompt_tmpl_str = ( "原始查询如下:{query_str}" "我们提供了现有答案:{existing_answer}" "我们有机会通过下面的更多上下文来完善现有答案(仅在需要时)。" "------------" "{context_msg}" "------------" "考虑到新的上下文,优化原始答案以更好地回答查询。 如果上下文没有用,请返回原始答案。" "Refined Answer:" ) refine_prompt_tmpl = PromptTemplate(refine_prompt_tmpl_str) # 使用llama-index-llm-huggingface调用本地大模型 Settings.llm = HuggingFaceLLM( context_window = 4096, max_new_tokens = 2048, generate_kwargs = {"temperature": 0.0, "do_sample": False}, query_wrapper_prompt = query_wrapper_prompt, tokenizer_name = "/home/kevin/projects/models/Qwen/Qwen1.5-7B-Chat", model_name = "/home/kevin/projects/models/Qwen/Qwen1.5-7B-Chat", device_map = "auto", model_kwargs = {"torch_dtype": torch.float16}, ) # 使用LlamaDebugHandler构建事件回溯器,以追踪LlamaIndex执行过程中发生的事件 llama_debug = LlamaDebugHandler(print_trace_on_end=True) callback_manager = CallbackManager([llama_debug]) Settings.callback_manager = callback_manager # 使用llama-index-embeddings-huggingface调用本地embedding模型 Settings.embed_model = HuggingFaceEmbedding( model_name="/home/kevin/projects/models/BAAI/bge-base-zh-v1.5" ) # 从存储文件中读取embedding向量和向量索引 storage_context = StorageContext.from_defaults(persist_dir="doc_emb") index = load_index_from_storage(storage_context) # 构建查询引擎 query_engine = index.as_query_engine(similarity_top_k=5) # 输出查询引擎中所有的prompt类型 prompts_dict = query_engine.get_prompts() print(list(prompts_dict.keys())) # 更新查询引擎中的prompt template query_engine.update_prompts( { "response_synthesizer:text_qa_template": qa_prompt_tmpl, "response_synthesizer:refine_template": refine_prompt_tmpl } ) # 查询获得答案 response = query_engine.query("不耐疲劳,口燥、咽干可能是哪些证候?") print(response) # 输出formatted_prompt event_pairs = llama_debug.get_llm_inputs_outputs() print(event_pairs[0][1].payload["formatted_prompt"]) ``` ## 十、RAG 系统评估 *使用 Ragas对进行系统评估,并给出评估指标!*
李智
2025年9月29日 17:19
转发文档
收藏文档
上一篇
下一篇
手机扫码
复制链接
手机扫一扫转发分享
复制链接
Markdown文件
分享
链接
类型
密码
更新密码