MySQL进阶
01、MySQL进阶:剖析MySQL索引底层数据结构
02、MySQL进阶:MySQL不同存储引擎下索引的实现
03、MySQL进阶:Explain深度剖析
04、MySQL进阶:践行索引优化
05、MySQL进阶:锁等待及死锁初探
06、MySQL进阶:无索引行锁升级为表锁
07、MySQL进阶:共享锁和排它锁初探
08、MySQL进阶:索引优化案例实操
09、MySQL进阶:索引下推IndexConditionPushdown初探
10、MySQL进阶:使用trace工具来窥探MySQL是如何选择执行计划的
11、MySQL进阶:orderby和groupby优化初探
12、MySQL进阶:分页查询优化的两个案例解析
13、MySQL进阶:Join关联查询优化
14、MySQL进阶:In和Exists的优化案例讲解
15、MySQL进阶:存储引擎初探
16、MySQL进阶:体系结构初探
17、MySQL进阶:解读MySQL事务与锁机制
18、MySQL进阶:多版本控制MVCC机制初探
19、MySQL进阶:并发事务问题及解决方案
20、MySQL进阶:锁机制初探
21、MySQL进阶:高效的设计MySQL库表
22、MySQL进阶:库表设计之IP和TIMESTAMP的处理
23、MySQL进阶:orderby出现usingfilesort根因分析及优化
24、MySQL进阶:canal实现mysql数据同步到redis|实现自定义canal客户端
本文档使用 MrDoc 发布
-
+
首页
10、MySQL进阶:使用trace工具来窥探MySQL是如何选择执行计划的
### **Pre** 有的时候,明明某个字段有索引,那我们一般认为走索引好一些,结果mysql走了全表扫描 , 那怎么看mysql是怎么选择的呢? 来 今天来看一看MySQL是如何循着合适的执行计划的? ------------ ### **演示Demo** 还是那个老表 employees ```python CREATE TABLE employees ( id int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, name varchar(24) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '姓名', age int(11) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '年龄', position varchar(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '职位', hire_time timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '入职时间', PRIMARY KEY (id), KEY idx_name_age_position (name,age,position) USING BTREE ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT='员工记录表'; ``` 来看个执行计划 ```python mysql> EXPLAIN select * from employees where name > 'a'; +----+-------------+-----------+------------+------+-----------------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+-------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-----------+------------+------+-----------------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+-------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | employees | NULL | ALL | idx_name_age_position | NULL | NULL | NULL | 100175 | 50 | Using where | +----+-------------+-----------+------------+------+-----------------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+-------------+ 1 row in set ```  推测一下,为何走了全表扫描 参考这篇文章 [MySQL - 索引优化案例实操 # Case 1 : 联合索引第一个字段用范围不一定会走索引](https://blog.csdn.net/yangshangwei/article/details/107753153) name > ‘a’ , 一般都不会用到索引。 如果用name索引需要遍历name字段联合索引树,然后还需要根据遍历出来的主键值去主键索引树里再去查出最终数据,成本比全表扫描还高 。 ------------ 优化呢? 1、 强制走索引(不一定效率高); 2、 使用覆盖索引,这样**只需要遍历name字段的联合索引树就能拿到所有结果**,来看下; ```python mysql> EXPLAIN select name,age,position from employees where name > 'a' ; +----+-------------+-----------+------------+-------+-----------------------+-----------------------+---------+------+-------+----------+--------------------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-----------+------------+-------+-----------------------+-----------------------+---------+------+-------+----------+--------------------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | employees | NULL | range | idx_name_age_position | idx_name_age_position | 74 | NULL | 50087 | 100 | Using where; Using index | +----+-------------+-----------+------------+-------+-----------------------+-----------------------+---------+------+-------+----------+--------------------------+ 1 row in set mysql> ``` 再来看个执行计划 ,仅仅把比对的value 换一下 ```python mysql> EXPLAIN select * from employees where name > 'zzz' ; +----+-------------+-----------+------------+-------+-----------------------+-----------------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-----------+------------+-------+-----------------------+-----------------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | employees | NULL | range | idx_name_age_position | idx_name_age_position | 74 | NULL | 1 | 100 | Using index condition | +----+-------------+-----------+------------+-------+-----------------------+-----------------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+ 1 row in set ```  搞得我一脸懵逼。。。。。 这样也行? 很明显,第二个 > zzz , key_len=74 = 3 * 24(表定义的varch长度) +2 , 使用了联合索引中的name , Extra也可以知一二,使用了部分索引条件。 那咋办? 到底是为啥? 仅仅是因为value的变化,导致mysql选择了不同的执行计划? ### **trace工具使用** ------------ 开启trace工具会影响mysql性能,所以只能临时分析sql使用,用完之后立即关闭 . ```python mysql> set session optimizer_trace="enabled=on",end_markers_in_json=on; --开启trace mysql> select * from employees where name > 'a' order by position; --- 执行SQL mysql> SELECT * FROM information_schema.OPTIMIZER_TRACE; ---查看trace mysql> set session optimizer_trace="enabled=off"; --关闭trace ``` **第二条和第三条 一起执行 ,切记** ------------ ### **Trace分析** 把结果copy出来  三大步 1、 准备阶段; 2、 优化阶段; 3、 执行阶段; 重点呢就是第二步 优化阶段 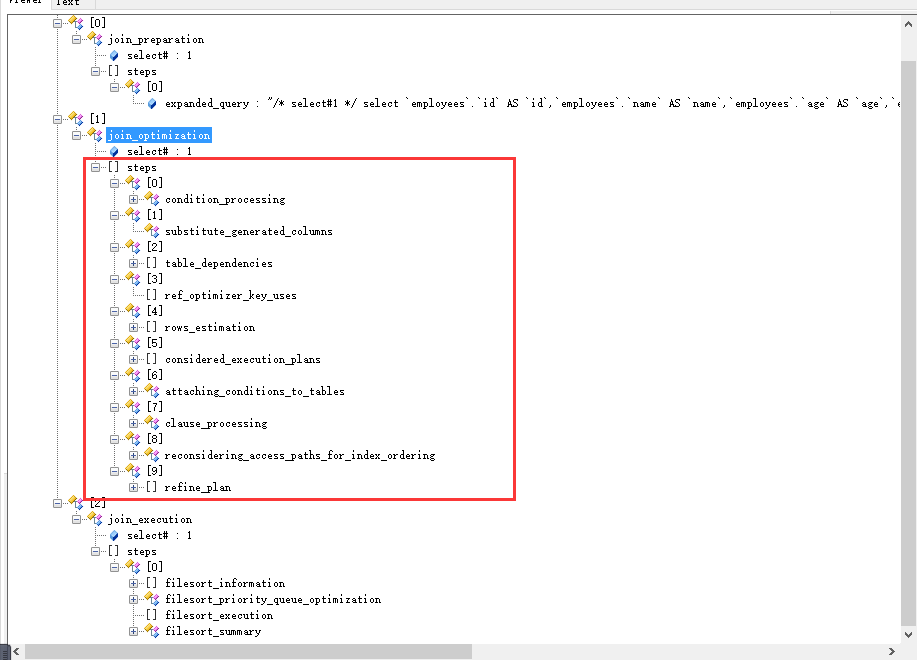 ### **Trace解读** ```python { "steps": [ { "join_preparation": { ---优化准备工作 "select#": 1, "steps": [ { "expanded_query": "/* select#1 */ select employees.id AS id,employees.name AS name,employees.age AS age,employees.position AS position,employees.hire_time AS hire_time from employees where (employees.name >` 'a') order by employees.position" } ] /* steps */ } /* join_preparation */ }, { "join_optimization": { ---- 优化阶段 "select#": 1, "steps": [ { "condition_processing": { ---- 条件处理 "condition": "WHERE", "original_condition": "(employees.name >` 'a')", "steps": [ { "transformation": "equality_propagation", "resulting_condition": "(employees.name >` 'a')" }, { "transformation": "constant_propagation", "resulting_condition": "(employees.name >` 'a')" }, { "transformation": "trivial_condition_removal", "resulting_condition": "(employees.name >` 'a')" } ] /* steps */ } /* condition_processing */ }, { "substitute_generated_columns": { } /* substitute_generated_columns */ }, { "table_dependencies": [ ------表依赖情况分析 { "table": "employees", "row_may_be_null": false, "map_bit": 0, "depends_on_map_bits": [ ] /* depends_on_map_bits */ } ] /* table_dependencies */ }, { "ref_optimizer_key_uses": [ ] /* ref_optimizer_key_uses */ }, { "rows_estimation": [ --- 预估表的访问成本 { "table": "employees", "range_analysis": { "table_scan": { ---全表扫描 "rows": 100175, --- 扫描的行数 "cost": 20390 ---COST查询成本 } /* table_scan */, "potential_range_indexes": [ --- 潜在的可以使用的索引 { "index": "PRIMARY", ---主键索引 "usable": false, "cause": "not_applicable" }, { "index": "idx_name_age_position", ---- 辅助索引 "usable": true, "key_parts": [ "name", "age", "position", "id" ] /* key_parts */ } ] /* potential_range_indexes */, "setup_range_conditions": [ ] /* setup_range_conditions */, "group_index_range": { "chosen": false, "cause": "not_group_by_or_distinct" } /* group_index_range */, "analyzing_range_alternatives": { --- 分析各个索引的使用成本 "range_scan_alternatives": [ { "index": "idx_name_age_position", "ranges": [ "a < name" ] /* ranges */, "index_dives_for_eq_ranges": true, "rowid_ordered": false, --使用该索引获取的记录是否按照主键排序 "using_mrr": false, "index_only": false, --- 是否使用覆盖索引 "rows": 50087, ---索引扫描行数 "cost": 60105, ---所用COST成本 "chosen": false, ---是否选择该索引 "cause": "cost" ---原因 } ] /* range_scan_alternatives */, "analyzing_roworder_intersect": { "usable": false, "cause": "too_few_roworder_scans" } /* analyzing_roworder_intersect */ } /* analyzing_range_alternatives */ } /* range_analysis */ } ] /* rows_estimation */ }, { "considered_execution_plans": [ -----建议执行计划 { "plan_prefix": [ ] /* plan_prefix */, "table": "employees", "best_access_path": { ---- 最优访问路径 "considered_access_paths": [ ---- 最终选择的访问路径 { "rows_to_scan": 100175, "access_type": "scan", --- 访问类型 scan 即全表扫描 "resulting_rows": 100175, "cost": 20388, "chosen": true, ------ true 确定选择 "use_tmp_table": true } ] /* considered_access_paths */ } /* best_access_path */, "condition_filtering_pct": 100, "rows_for_plan": 100175, "cost_for_plan": 20388, "sort_cost": 100175, "new_cost_for_plan": 120563, "chosen": true } ] /* considered_execution_plans */ }, { "attaching_conditions_to_tables": { "original_condition": "(employees.name >` 'a')", "attached_conditions_computation": [ ] /* attached_conditions_computation */, "attached_conditions_summary": [ { "table": "employees", "attached": "(employees.name >` 'a')" } ] /* attached_conditions_summary */ } /* attaching_conditions_to_tables */ }, { "clause_processing": { "clause": "ORDER BY", "original_clause": "employees.position", "items": [ { "item": "employees.position" } ] /* items */, "resulting_clause_is_simple": true, "resulting_clause": "employees.position" } /* clause_processing */ }, { "reconsidering_access_paths_for_index_ordering": { "clause": "ORDER BY", "steps": [ ] /* steps */, "index_order_summary": { "table": "employees", "index_provides_order": false, "order_direction": "undefined", "index": "unknown", "plan_changed": false } /* index_order_summary */ } /* reconsidering_access_paths_for_index_ordering */ }, { "refine_plan": [ { "table": "employees" } ] /* refine_plan */ } ] /* steps */ } /* join_optimization */ }, { "join_execution": { ----- 阶段三 执行SQL "select#": 1, "steps": [ { "filesort_information": [ { "direction": "asc", "table": "employees", "field": "position" } ] /* filesort_information */, "filesort_priority_queue_optimization": { "usable": false, "cause": "not applicable (no LIMIT)" } /* filesort_priority_queue_optimization */, "filesort_execution": [ ] /* filesort_execution */, "filesort_summary": { "rows": 100003, "examined_rows": 100003, "number_of_tmp_files": 31, "sort_buffer_size": 262056, "sort_mode": "<sort_key, packed_additional_fields>" } /* filesort_summary */ } ] /* steps */ } /* join_execution */ } ] /* steps */ } ``` MySQL认为 全表扫描的成本低于索引扫描,所以mysql最终选择全表扫描 。 ------------ 同样的看看看 zzz的 ```python mysql> set session optimizer_trace="enabled=on",end_markers_in_json=on; --开启trace mysql> select * from employees where name > 'zzz' order by position; --- 执行SQL mysql> SELECT * FROM information_schema.OPTIMIZER_TRACE; ---查看trace mysql> set session optimizer_trace="enabled=off"; --关闭trace ``` 同样的套路,我相信你也能看出一二
李智
2025年3月17日 13:31
转发文档
收藏文档
上一篇
下一篇
手机扫码
复制链接
手机扫一扫转发分享
复制链接
Markdown文件
分享
链接
类型
密码
更新密码