MySQL进阶
01、MySQL进阶:剖析MySQL索引底层数据结构
02、MySQL进阶:MySQL不同存储引擎下索引的实现
03、MySQL进阶:Explain深度剖析
04、MySQL进阶:践行索引优化
05、MySQL进阶:锁等待及死锁初探
06、MySQL进阶:无索引行锁升级为表锁
07、MySQL进阶:共享锁和排它锁初探
08、MySQL进阶:索引优化案例实操
09、MySQL进阶:索引下推IndexConditionPushdown初探
10、MySQL进阶:使用trace工具来窥探MySQL是如何选择执行计划的
11、MySQL进阶:orderby和groupby优化初探
12、MySQL进阶:分页查询优化的两个案例解析
13、MySQL进阶:Join关联查询优化
14、MySQL进阶:In和Exists的优化案例讲解
15、MySQL进阶:存储引擎初探
16、MySQL进阶:体系结构初探
17、MySQL进阶:解读MySQL事务与锁机制
18、MySQL进阶:多版本控制MVCC机制初探
19、MySQL进阶:并发事务问题及解决方案
20、MySQL进阶:锁机制初探
21、MySQL进阶:高效的设计MySQL库表
22、MySQL进阶:库表设计之IP和TIMESTAMP的处理
23、MySQL进阶:orderby出现usingfilesort根因分析及优化
24、MySQL进阶:canal实现mysql数据同步到redis|实现自定义canal客户端
本文档使用 MrDoc 发布
-
+
首页
08、MySQL进阶:索引优化案例实操
 ### **DB Version** ```python mysql> select version(); +------------+ | version() | +------------+ | 5.7.29-log | +------------+ 1 row in set ``` 默认隔离级别 RR 可重复读 ------------ ### **Table** ```python CREATE TABLE employees ( id int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, name varchar(24) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '姓名', age int(11) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '年龄', position varchar(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '职位', hire_time timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '入职时间', PRIMARY KEY (id), KEY idx_name_age_position (name,age,position) USING BTREE ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT='员工记录表'; ``` 重点 1、 主键id PRIMARYKEY(id) ; 2、 联合索引 KEYidx_name_age_position(name,age,position) USINGBTREE; 我们向表里写入10万来条数据 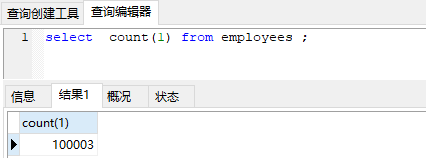 ------------ ### Case 1 : 联合索引第一个字段用范围不一定会走索引  ```python mysql> EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM employees WHERE name > 'LiLei' AND age = 22 AND position ='manager'; +----+-------------+-----------+------------+-------+-----------------------+-----------------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-----------+------------+-------+-----------------------+-----------------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | employees | NULL | range | idx_name_age_position | idx_name_age_position | 74 | NULL | 1 | 5 | Using index condition | +----+-------------+-----------+------------+-------+-----------------------+-----------------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+ 1 row in set mysql> EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM employees WHERE name > 'Artisan' AND age = 22 AND position ='manager'; +----+-------------+-----------+------------+------+-----------------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+-------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-----------+------------+------+-----------------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+-------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | employees | NULL | ALL | idx_name_age_position | NULL | NULL | NULL | 100175 | 0.5 | Using where | +----+-------------+-----------+------------+------+-----------------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+-------------+ 1 row in set mysql> ``` 当然了,也不是所有的情况都不走索引, MySQL会基于Cost选择一个合适的 ,如果没有走索引,可能mysql内部可能觉得第一个字段就用范围,结果集应该很大,回表效率不高,还不如就全表扫描 如果没有走索引想要去优化的话怎么办呢? ------------ ### 优化一 强制走索引 force index(idx_name_age_position) ```python mysql> EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM employees force index(idx_name_age_position) WHERE name > 'Artisan' AND age = 22 AND position ='manager'; +----+-------------+-----------+------------+-------+-----------------------+-----------------------+---------+------+-------+----------+-----------------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-----------+------------+-------+-----------------------+-----------------------+---------+------+-------+----------+-----------------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | employees | NULL | range | idx_name_age_position | idx_name_age_position | 74 | NULL | 50087 | 1 | Using index condition | +----+-------------+-----------+------------+-------+-----------------------+-----------------------+---------+------+-------+----------+-----------------------+ 1 row in set ```  ### 优化二 覆盖索引优化 ```python mysql> EXPLAIN SELECT name , age , position FROM employees WHERE name > 'Artisan' AND age = 22 AND position ='manager'; +----+-------------+-----------+------------+-------+-----------------------+-----------------------+---------+------+-------+----------+--------------------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-----------+------------+-------+-----------------------+-----------------------+---------+------+-------+----------+--------------------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | employees | NULL | range | idx_name_age_position | idx_name_age_position | 74 | NULL | 50087 | 1 | Using where; Using index | +----+-------------+-----------+------------+-------+-----------------------+-----------------------+---------+------+-------+----------+--------------------------+ 1 row in set mysql> ``` 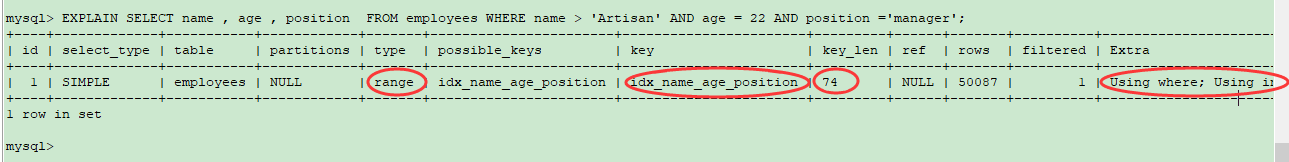 name , age , position 是联合索引,在索引树上,同时索引树上的叶子节点还会关联一个主键id , 如果查询 * 的话,还要根据id去主键索引上去查找其他字段,需要回表, 如果仅查询二级索引树idx_name_age_position上的字段,那就无需回表操作了,效率自然高一些。 ------------ ### Case 2 : in和or在表数据量比较大的情况会走索引,在表记录不多的情况下会选择全表扫描 ```python mysql> EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM employees WHERE name in ('LiLei','HanMeimei','Lucy') AND age = 22 AND position ='manager'; +----+-------------+-----------+------------+-------+-----------------------+-----------------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-----------+------------+-------+-----------------------+-----------------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | employees | NULL | range | idx_name_age_position | idx_name_age_position | 140 | NULL | 3 | 100 | Using index condition | +----+-------------+-----------+------------+-------+-----------------------+-----------------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+ 1 row in set mysql> EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM employees WHERE (name = 'LiLei' or name = 'HanMeimei') AND age = 22 AND position ='manager'; +----+-------------+-----------+------------+-------+-----------------------+-----------------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-----------+------------+-------+-----------------------+-----------------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | employees | NULL | range | idx_name_age_position | idx_name_age_position | 140 | NULL | 2 | 100 | Using index condition | +----+-------------+-----------+------------+-------+-----------------------+-----------------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+ 1 row in set ```  再搞个小表 ,和 employees 一模一样哈,连索引也得一样,插入3条数据 。 ```python CREATE TABLE employees_2 ( id int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, name varchar(24) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '姓名', age int(11) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '年龄', position varchar(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '职位', hire_time timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '入职时间', PRIMARY KEY (id), KEY idx_name_age_position (name,age,position) USING BTREE ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT='员工记录表'; INSERT INTO employees_2(name,age,position,hire_time) VALUES('LiLei',22,'manager',NOW()); INSERT INTO employees_2(name,age,position,hire_time) VALUES('HanMeimei', 23,'dev',NOW()); INSERT INTO employees_2(name,age,position,hire_time) VALUES('Lucy',23,'dev',NOW()); ``` 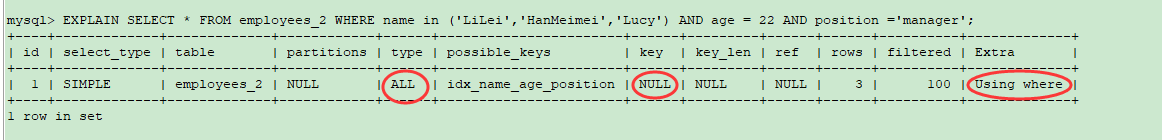 ```python mysql> EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM employees_2 WHERE name in ('LiLei','HanMeimei','Lucy') AND age = 22 AND position ='manager'; +----+-------------+-------------+------------+------+-----------------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------------+------------+------+-----------------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | employees_2 | NULL | ALL | idx_name_age_position | NULL | NULL | NULL | 3 | 100 | Using where | +----+-------------+-------------+------------+------+-----------------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+ 1 row in set mysql> ``` **为什么呢? 就几条数据的话, 结合B+树的结构, MySQL认为从根节点开始向下找,还不如直接从叶子节点从头开始扫描快呢** ------------ ### **Case 3 : like KK% 一般情况都会走索引** 结合索引树 , like KK% 可以理解为就是按照 = KK 查询 ```python mysql> EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM employees WHERE name like 'LiLei%' AND age = 22 AND position ='manager'; +----+-------------+-----------+------------+-------+-----------------------+-----------------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-----------+------------+-------+-----------------------+-----------------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | employees | NULL | range | idx_name_age_position | idx_name_age_position | 140 | NULL | 1 | 5 | Using index condition | +----+-------------+-----------+------------+-------+-----------------------+-----------------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+ 1 row in set mysql> EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM employees_2 WHERE name like 'LiLei%' AND age = 22 AND position ='manager'; +----+-------------+-------------+------------+-------+-----------------------+-----------------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------------+------------+-------+-----------------------+-----------------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | employees_2 | NULL | range | idx_name_age_position | idx_name_age_position | 140 | NULL | 1 | 33.33 | Using index condition | +----+-------------+-------------+------------+-------+-----------------------+-----------------------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------+ 1 row in set ``` ------------ ### **特殊例子** 一般情况 ,但也不绝对。看下面这个例子 假设你这个表 的name字段 是以Artisan开头的,从Artisan1 到Artisan100000 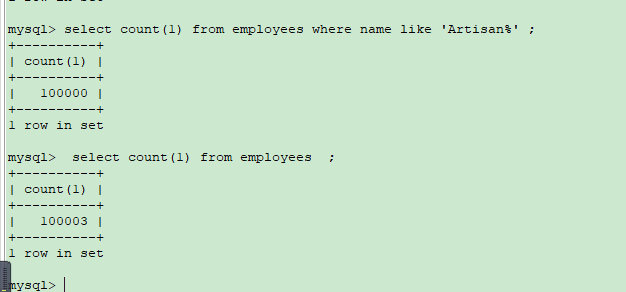 再去like的话 ,mysql会基于cost,自主选择 ,比如如下走了全表扫描。 
李智
2025年3月17日 13:31
转发文档
收藏文档
上一篇
下一篇
手机扫码
复制链接
手机扫一扫转发分享
复制链接
Markdown文件
分享
链接
类型
密码
更新密码